Essential Insights into guide to Blockchain Technology for Beginners

The digital landscape has evolved dramatically over the past decade, giving rise to an innovative framework that challenges traditional notions of record-keeping and data management. This novel approach is characterized by its unique ability to provide transparent and secure transactions, making it an alluring subject for both novices and enthusiasts alike. As more individuals and organizations delve into this realm, it becomes essential to grasp the key concepts driving its adoption and expansion.
At its core, this paradigm represents a shift towards decentralization, allowing information to be shared across a network of participants without the need for a central authority. This revolutionary model not only enhances security but also fosters trust among users, as records become immutable and verifiable. As we explore the fundamental principles and mechanics behind this system, we will uncover the reasons behind its rapid integration into various sectors, from finance to supply chain management.
As you embark on this journey through the intricate world of distributed ledgers, you will encounter a wealth of information that illuminates the specific components and benefits of this innovative framework. By the end of this exploration, you’ll possess a solid foundation that equips you to engage with this transformative phenomenon confidently.
What is Blockchain Technology?
This innovative digital ledger concept is transforming various industries by allowing secure and transparent record-keeping. Its decentralized structure eliminates the need for intermediaries, fostering a new level of trust among participants. Such a system supports numerous applications, from financial transactions to supply chain management, and promotes accountability at every stage.
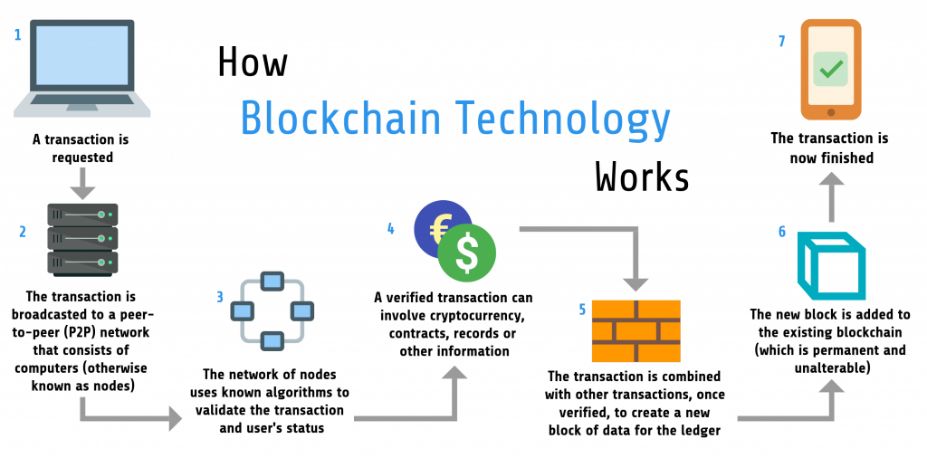
At its core, this mechanism relies on a series of interconnected blocks, each containing a set of transactions. These blocks are linked together in a chronological manner, creating an immutable chain that safeguards data integrity. Here are some key characteristics of this approach:
- Decentralization: No single entity controls the network, reducing the risk of fraud.
- Transparency: All participants can view the record, fostering openness.
- Immutability: Once information is added, it cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring reliability.
- Security: Advanced cryptographic techniques protect data from unauthorized access.
This framework is already being utilized across multiple sectors, showcasing its versatility and potential. As organizations continue to explore its capabilities, we may witness significant shifts in how we approach transactions and data management.
Key Features of Blockchain Systems
This section delves into the essential characteristics that define distributed ledger frameworks. These attributes not only differentiate them from traditional systems but also contribute to their growing relevance and application across various sectors. Understanding these features can provide insights into the potential and functionalities these frameworks offer.
Decentralization
One of the most significant aspects of distributed ledgers is their decentralized nature. This means that no single entity has control over the entire network. Here are some implications of decentralization:
- Reduced risk of single points of failure.
- Increased security as data is replicated across multiple nodes.
- Enhanced transparency since every participant can access the same information.
Immutability
An essential trait of these systems is immutability, which refers to the inability to alter records once they are confirmed. This feature is crucial for various reasons:
- Promotes trust among users, as past transactions cannot be tampered with.
- Facilitates auditability, making it easier to track changes over time.
- Enhances data integrity, ensuring that the information remains consistent and accurate.
These characteristics underscore the robustness of distributed ledgers, highlighting why many industries are exploring their capabilities for improving efficiency and security.
How Blockchain Ensures Data Security
The advent of this innovative system has brought forth a paradigm shift in how information is recorded and maintained. Leveraging a unique architecture, it ensures that data remains intact, unaltered, and trustworthy. This integrity is crucial in an era where cyber threats are rampant and data breaches have become commonplace.
Decentralization and Its Role
One of the fundamental principles of this system is decentralization. Unlike traditional databases that are controlled by centralized entities, data in this structure is distributed across numerous nodes. This eliminates the single point of failure, making it significantly harder for malicious actors to manipulate or corrupt the information.
Encryption and Immutability
In addition to decentralization, strong encryption techniques are employed to safeguard data. Each data block is cryptographically linked to the previous one, creating a secure chain. Once a block is added, it is virtually impossible to alter without affecting all subsequent blocks, thereby preserving the authenticity of the entire chain. This combination of features not only fortifies security but also enhances trust among users who rely on the accuracy of the stored information.

Applications of Blockchain in Various Industries
The innovative ledger system is transforming multiple sectors by offering transparency, security, and efficiency. Its unique characteristics enable various organizations to streamline operations, enhance trust among stakeholders, and reduce costs. As a result, many fields are exploring the implementation of this decentralized method to solve traditional challenges.
Finance: In the financial sector, the distributed ledger approach facilitates quicker transactions, lower fees, and increased security. For example, cryptocurrencies allow for borderless payments, while smart contracts automate financial agreements without intermediaries.
Supply Chain: The application of this system in supply chains enhances traceability and accountability. Organizations can monitor products from production to delivery, ensuring quality and authenticity. This transparency helps to mitigate fraud and reduce inefficiencies.
Healthcare: In healthcare, the decentralized framework can safely store patient records while maintaining privacy. It allows for seamless sharing of medical data among practitioners, improving patient care and reducing administrative burdens.
Real Estate: The real estate market benefits from this technology by simplifying property transactions and record-keeping. Smart contracts can automate the transfer of ownership, reducing paperwork and expediting the process.
Energy: In the energy sector, decentralized solutions allow for peer-to-peer energy trading. Consumers can buy and sell excess energy directly, leading to more efficient usage and greater sustainability.
Overall, the adoption of this innovative ledger method is gaining momentum across various industries, revolutionizing operations and paving the way for a more secure and efficient future.
Smart Contracts and Their Functionality
In the realm of decentralized systems, the concept of self-executing agreements has gained significant attention. These digital arrangements operate without the need for intermediaries, promising enhanced trust and efficiency in transactions. Their design allows for automation of processes, reducing human intervention while ensuring that all parties adhere to the stipulated conditions.
Core Features of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are characterized by their ability to automatically execute actions when predefined conditions are met. This feature is made possible through programmed logic, which eliminates ambiguity and enhances reliability. Once deployed on a network, the terms are immutable, ensuring that no party can alter the agreement without consensus.
Applications Across Industries
The utility of smart contracts extends across various sectors, including finance, supply chain management, and real estate. In financial services, they facilitate seamless transactions, allowing for instant settlements. In supply chains, they enhance transparency and traceability, ensuring that every step of the process is documented and verified. Additionally, in real estate, these contracts simplify property transfers, minimizing paperwork and expediting closings.
Overall, the rise of self-executing agreements represents a transformative shift in how entities interact and transact, fostering a new era of efficiency and trust in digital dealings.
Future Trends in Blockchain Development
As we look ahead, the evolution of decentralized systems is poised to reshape various industries and transform the way we conduct transactions and manage data. Emerging trends suggest a shift towards greater scalability, interoperability, and enhanced security, promising a more efficient and integrated ecosystem.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is expected to gain more traction, providing individuals with more direct access to financial services, while reducing reliance on traditional banking institutions. This movement aims to democratize finance by offering innovative solutions that cater to a wider audience.
Another significant trend is the rise of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs). These unique digital assets are changing the landscape of ownership, particularly in the realms of art, gaming, and virtual real estate. The potential for tokenization to represent both tangible and intangible assets will likely continue to expand, fostering new opportunities for creators and consumers alike.
Moreover, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) with decentralized ledgers is anticipated to create smarter, more efficient systems. Combining these two advanced technologies can enhance data analytics, optimize decision-making processes, and facilitate automation across various applications.
As regulators worldwide begin to clarify their positions on decentralized networks, increased legal frameworks can further legitimize this field. This clarity may encourage more businesses to explore the advantages offered by distributed ledgers, leading to broader adoption and innovative use cases.
In conclusion, the future of decentralized systems appears vibrant, marked by innovation and a potential shift in societal norms. The continued exploration of new applications will not only heighten interest but also inspire further advancements in this rapidly developing arena.
Q&A: Beginners guide to blockchain technology
What is blockchain technology and how does it work?
Blockchain technology is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger system that securely records transactions across many computers. The main components of blockchain include blocks, which contain transaction data, a cryptographic hash of the previous block, and a timestamp. When a new transaction occurs, it is grouped with others into a block and added to the chain in chronological order. This process is safeguarded by cryptography, making it nearly impossible to alter the recorded data without the consensus of the network, thereby enhancing security and transparency.
What are the key benefits of using blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology offers several key benefits, including increased security, transparency, and efficiency. Because of its decentralized nature, there is no single point of failure, making it less susceptible to hacking or fraud. Transactions are recorded in a public ledger that can be verified by all participants, promoting transparency and trust. Additionally, blockchain can streamline processes by reducing intermediaries, thereby speeding up transactions and reducing costs. It’s particularly beneficial in sectors like finance, supply chain, and healthcare.
Can blockchain technology be hacked, and what are the security measures in place to protect it?
While no system is entirely immune to hacking, blockchain is designed with multiple security features. Each block is linked to the previous block through a cryptographic hash, making it extremely difficult to alter any information without altering all subsequent blocks, which would require the consensus of the majority of the network participants, known as nodes. Additionally, many blockchains use consensus algorithms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake, which enhance security by ensuring that transactions are validated and confirmed by multiple parties before being added to the chain.
What are some common use cases for blockchain technology beyond cryptocurrencies?
Beyond cryptocurrencies, blockchain technology is being utilized in various industries for multiple use cases. In supply chain management, it enables real-time tracking of goods, ensuring transparency and reducing fraud. In healthcare, blockchain can securely store patient records, allowing for better data sharing between healthcare providers while maintaining patient privacy. Other use cases include smart contracts in real estate transactions, digital identity verification, and voting systems to enhance security and trust in electoral processes. Essentially, any domain that relies on trusted records can benefit from blockchain technology.
How can I start learning about blockchain technology as a beginner?
As a beginner looking to learn about blockchain technology, there are several resources and steps you can take. Start by reading introductory articles and watching educational videos to grasp the basics. Websites like Coursera and edX offer free courses on blockchain fundamentals. Joining online communities, such as forums and social media groups focused on blockchain, can also provide valuable insights and networking opportunities. Additionally, consider experimenting with blockchain coding through platforms like Ethereum or Hyperledger, which offer documentation and tutorials for getting started with smart contracts and decentralized applications.
What is blockchain, and how does it work?
Blockchain is a digital ledger technology that records transactions on the blockchain in a decentralized and transparent manner. Each transaction is verified by a network of computers, grouped into a new block, and then added to the blockchain. This chain of blocks is immutable, making blockchain technology reliable for various applications, from cryptocurrencies like bitcoin to smart contracts on the ethereum blockchain.
What are the different types of blockchain, and how do they compare?
There are three main types of blockchain: public blockchain, private blockchain, and consortium blockchain. A public blockchain, like bitcoin and ethereum, is open to anyone and fully decentralized. A private blockchain is restricted to specific participants, offering more control but less transparency. Consortium blockchains are governed by a group of organizations, combining elements of both public and private blockchains to balance decentralization and privacy.
How is the decentralized nature of blockchain beneficial for cryptocurrencies like bitcoin?
The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures that no single entity controls the entire blockchain, increasing security and reducing the risk of fraud. In cryptocurrencies like bitcoin, this decentralized system allows peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries. By distributing data across a network of computers, blockchain technology provides transparency, security, and trust in digital currencies.
What are some common blockchain applications beyond cryptocurrencies?
Blockchain applications extend beyond cryptocurrencies like bitcoin and ethereum to industries such as supply chain management, healthcare, and finance. Blockchain enables secure, tamper-proof record-keeping, making it ideal for tracking goods, managing medical records, and processing financial transactions. The use of blockchain in these sectors highlights its potential to enhance transparency, reduce costs, and improve operational efficiency.
What are the potential disadvantages of blockchain technology?
Despite its many advantages, blockchain technology has some disadvantages. The decentralized nature of blockchain can lead to scalability issues, as each transaction must be verified by the entire blockchain network. Additionally, blockchain transactions can be energy-intensive, particularly in proof of work systems like the bitcoin blockchain. Another challenge is the lack of regulatory clarity, which may hinder broader adoption of blockchain platforms in certain industries.