Exploring Innovative DAO Governance Models

The rise of blockchain technology has ushered in a new era of interactive networks, characterized by a shift away from centralized authority. This transformation has led to the exploration of unique frameworks that empower participants to engage in shared governance. By leveraging decentralized systems, individuals can collectively navigate complex challenges, ensuring that every voice is heard and valued.
As digital platforms evolve, so do the strategies employed for leadership and collaboration. These approaches prioritize inclusivity and transparency, aiming to foster an environment where decisions reflect the collective will of community members. The integration of diverse perspectives not only enriches the discourse but also cultivates a sense of ownership among participants.
Understanding the intricacies of these frameworks is crucial for enhancing collaboration and resilience within digital communities. As stakeholders seek to establish clear roles, responsibilities, and processes, the effectiveness of such architectures will be pivotal in determining their long-term success. By examining different frameworks, we can uncover valuable insights that may guide future developments in shared decision-making.
Understanding DAO Governance Frameworks
The structure and processes that guide the decision-making within decentralized entities play a crucial role in their success. By establishing a common set of rules and collaborative practices, these frameworks ensure that all participants can contribute effectively while aligning with the entity’s overarching goals. Different approaches can lead to diverse outcomes, making it essential to understand the variety of frameworks available.
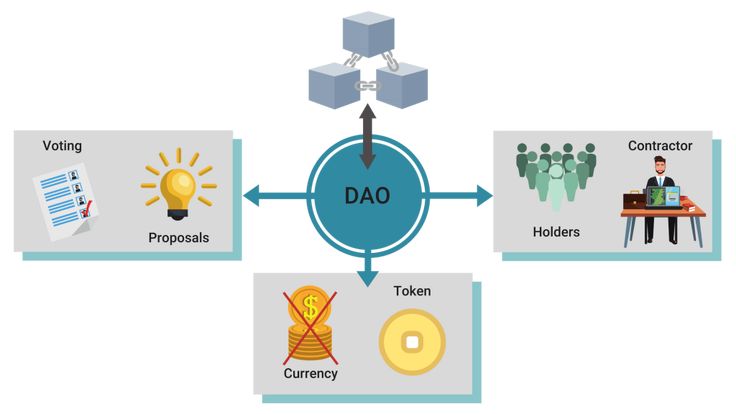
Key Components of Governance Structures
- Decision-Making Processes: The methods through which proposals are initiated, discussed, and voted on.
- Incentive Mechanisms: Rewards and penalties that motivate participant engagement and compliance with the framework.
- Transparency Measures: Practices that ensure all actions and decisions are open to scrutiny, fostering trust among participants.
- Dispute Resolution: Systems in place to address conflicts and disagreements within the community, ensuring stability and fairness.
Diverse Approaches to Governance
Various frameworks can be adopted by these entities, each with its unique characteristics:
- Representative Governance: A model where elected representatives make decisions on behalf of the participants.
- Direct Democracy: Involving all members in every decision through votes, promoting inclusivity.
- Liquid Democracy: A hybrid approach allowing individuals to delegate their voting power while still participating directly when desired.
Understanding the intricacies of these governance systems is vital for enhancing operational efficiency and participant satisfaction in decentralized frameworks.
The Role of Smart Contracts
In contemporary digital ecosystems, automated agreements serve as a cornerstone for streamlined interactions and transparent transactions. These algorithms govern a multitude of processes, ensuring that actions are executed without the influence of intermediaries. By embedding rules directly into the code, they enhance reliability and reliability in conducting business.
Smart contracts enable parties to negotiate terms and conditions in a secure manner, while minimizing disputes and enhancing trust. Their self-executing nature ensures compliance with agreed-upon rules, making manual oversight unnecessary. This faceless automation leads to a significant reduction in operational costs and time, allowing entities to concentrate on strategic activities instead of administrative tasks.
Furthermore, the use of these technological frameworks fosters a new level of transparency. All transactions are recorded on a blockchain, providing an immutable audit trail accessible to all participants. This visibility not only promotes accountability but also encourages collaboration among diverse stakeholders in the community.
Ultimately, such automated systems transform traditional practices by instilling a sense of fairness and efficiency. As more entities embrace this approach, the landscape of interactions is poised to evolve, paving the way for innovative practices and enhanced cooperation in collective endeavors.
Challenges in Decentralized Decision-Making
In recent years, collaborative decision-making processes have gained traction, promising a fairer distribution of power and authority. However, this shift comes with its own set of complexities and hurdles that need to be addressed. Understanding these issues is crucial for anyone involved in such adaptive structures, as they can influence the overall efficacy of the collective.
Coordination and Communication Barriers
One of the primary obstacles in shared decision-making environments is the challenge of communication among participants. As diverse individuals with varying backgrounds and expertise come together, establishing a common language becomes imperative yet often difficult. Misunderstandings and misalignments can lead to frustration, creating a rift within the group. Moreover, coordinating schedules and discussions in a global context, where members may reside in different time zones, adds another layer of complexity.
Consensus vs. Speed
Seeking unanimous agreement can be an admirable goal but often leads to delays in reaching conclusions. The pursuit of consensus may result in lengthy deliberations, causing important decisions to be postponed indefinitely. In contrast, the necessity to act swiftly in a rapidly changing environment can create tension. Striking a balance between ensuring inclusive participation and maintaining momentum is essential, but it is a delicate dance that tests the resilience of any collaborative effort.
Ultimately, the journey towards effective collective decision-making requires a solid understanding of these challenges and proactive strategies to mitigate them. Emphasizing clear communication and setting realistic timelines can pave the way for more harmonious and productive interactions among participants.
Community Participation and Engagement
The involvement of individuals in the decision-making process is crucial for the vitality of any collective endeavor. When members actively contribute to discussions and express their views, it fosters a sense of belonging and ownership. Engaged participants are more likely to support initiatives and drive progress, creating a dynamic environment where diverse ideas can flourish.
Importance of Inclusive Dialogue
In any collaborative setting, open channels of communication are vital. Providing platforms for dialogue ensures that all voices are heard, regardless of their background or experience. This inclusivity not only enriches the decision-making process but also nurtures trust among participants. When individuals feel valued and respected, their commitment to the community strengthens, leading to a more robust and resilient network.
Strategies for Enhancing Engagement
Implementing structured approaches can significantly boost participation levels. Regular meetings, online forums, and feedback mechanisms allow members to express their opinions and suggestions. Additionally, educational initiatives can empower participants with the knowledge to engage meaningfully. Recognizing contributions and celebrating achievements further motivates individuals, creating a positive feedback loop that encourages ongoing involvement.

Case Studies of Successful DAOs
This section delves into noteworthy examples that highlight how innovative community-led initiatives have thrived. By examining diverse instances, we can glean insights into their operational strategies and mechanisms that have contributed to their achievements. Each case showcases unique approaches tailored to their specific environments, allowing for a broader understanding of collaborative governance.
| Organization | Purpose | Key Features | Achievements |
|---|---|---|---|
| MolochDAO | Funding Ethereum projects | Simple membership, pledge-based funding | Significant funding for critical ecosystem projects |
| PleasrDAO | Acquire and manage digital art | Collaborative purchasing, community curation | Successful ownership of valuable NFTs, fostering art appreciation |
| BanklessDAO | Promote a decentralized financial future | Content creation, educational endeavors | Vast community engagement, educational resources for users |
| GitcoinDAO | Support open-source development | Quadratic funding, community voting | Substantial contributions to various projects, enhanced developer support |
These examples serve to illustrate the diverse ways in which communities can self-govern and drive collective progress. The lessons drawn from these cases are instrumental in shaping a promising future for collaborative initiatives.
Future Trends in DAO Governance
The landscape of community-led entities is evolving rapidly, driven by technological innovations and shifting societal attitudes towards coordination and management. As these collaborative frameworks mature, they are likely to adopt new practices and tools to enhance participation, transparency, and decision-making. Understanding these upcoming trends is crucial for stakeholders seeking to adapt and thrive in this dynamic ecosystem.
Enhanced Participatory Mechanisms
Future iterations of community leadership are expected to incorporate advanced participatory methods that encourage broader engagement. Tools such as quadratic voting and liquid democracy may gain traction, allowing members to express preferences more nuanced than a simple yes or no. This shift towards inclusive frameworks can strengthen community bonds and enhance the legitimacy of decisions made.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence
As artificial intelligence continues to advance, its integration into collaborative entities may revolutionize operations. AI can facilitate data analysis, automate administrative tasks, and assist in predictive modeling to inform decisions. By leveraging these technologies, members can focus on strategic initiatives rather than getting bogged down in routine processes, thereby fostering a more productive environment.
Ultimately, as community-driven ventures evolve, embracing innovation and adaptation will be key. Continuous exploration of emerging trends will enable participants to create and refine frameworks that are not only resilient but also aligned with the collective goals of their members.
Q&A: Dao governance models
What are DAO governance models, and why are they important for decentralized organizations?
DAO governance models refer to the frameworks and processes that decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) use to make decisions, manage resources, and oversee operations. These models are crucial because they enable collective decision-making and promote transparency, accountability, and inclusiveness within the organization. Effective governance ensures that all members have a voice in shaping the direction of the DAO, which helps build trust and encourages active participation. As decentralized organizations grow, having a well-structured governance model becomes essential for maintaining order, fostering innovation, and achieving long-term sustainability.
What are some common challenges faced by DAOs in implementing governance models?
DAOs often encounter several challenges when implementing governance models. One common issue is achieving consensus among diverse stakeholders, which can lead to gridlock if no agreement is reached. Additionally, balancing the interests of different member groups—such as developers, investors, and users—can create tensions and complicate decision-making processes. Furthermore, ensuring accountability can be difficult in a decentralized environment, where individuals may act with anonymity. Lastly, there is the challenge of adapting governance structures to scale as the DAO grows, which can impact efficiency and responsiveness. Addressing these challenges is crucial for the effectiveness and continued evolution of DAO governance.
Can you explain the difference between on-chain and off-chain governance in DAOs?
On-chain governance refers to decision-making processes that occur directly on the blockchain. This often involves voting mechanisms whereby token holders can vote on proposals using smart contracts, ensuring transparency and immutability. In contrast, off-chain governance involves discussions, deliberations, and decision-making that happen outside the blockchain environment, such as forums, social media, or in real-world meetings. Off-chain governance can be more flexible and allows for deeper discussions, but it may lack the same level of transparency and enforceability as on-chain processes. Each approach has its advantages and drawbacks, and many DAOs adopt a hybrid model that incorporates elements of both to optimize their governance.” (add length if required)
What role does community involvement play in DAO governance models?
Community involvement is a cornerstone of effective DAO governance. The success of a DAO largely depends on the active participation of its members, who contribute diverse perspectives, expertise, and resources. Engaging the community fosters a sense of ownership and investment in the organization’s success, which can lead to more innovative ideas and solutions. Moreover, when members feel their voices are heard and valued, it enhances trust and collaboration among stakeholders. Active participation can take many forms, such as voting on proposals, contributing to discussions, or even collaborating on initiatives. Ultimately, a vibrant community not only aids in decision-making but also strengthens the DAO’s overall identity and mission.
What are some of the most effective DAO governance models currently in use?
Several effective DAO governance models have emerged, showcasing a range of approaches tailored to different organizational needs. One well-known model is the delegation system, where token holders can delegate their voting power to representatives, enhancing engagement and expertise in decision-making. Another model is the multisig governance, which requires multiple key holders to approve transactions, increasing security and collective accountability. Some DAOs utilize a quadratic voting system, allowing members to express the intensity of their preferences by allocating votes differently, promoting more equitable decision-making. Additionally, reputation-based governance models reward community contributions with voting power, encouraging positive engagement. Each of these models has its strengths and can be chosen or adapted depending on the specific goals and structure of the DAO.
What are the key principles that define effective DAO governance models?
Effective DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) governance models are typically characterized by several key principles. Firstly, they emphasize decentralization, ensuring that no single entity has unilateral control over decision-making processes. This is crucial for maintaining trust among participants. Secondly, transparency is essential; all operations and decisions should be accessible to members, allowing for accountability. Thirdly, inclusivity is vital, as diverse input from a wide range of stakeholders can lead to more balanced and effective governance outcomes. Additionally, effective governance models often incorporate mechanisms for community participation, such as voting systems or consensus protocols, enabling members to have a direct say in organizational policies. Finally, adaptability is important, as DAO governance should evolve based on community feedback and changing circumstances, allowing organizations to remain relevant and effective over time.
How does decentralized governance work within the Ethereum Name Service (ENS) DAO?
Decentralized governance within the ENS DAO allows dao members to participate in decision-making processes regarding the Ethereum Name Service platform. Voting power is directly proportional to the number of tokens a member holds, meaning those with more tokens have a larger influence on governance decisions. This governance process is facilitated through token-based voting, where each voting right enables participation in key decisions about the future of ENS.
What are the different types of DAO governance models and how do they impact decision-making?
There are various types of DAO governance models, such as token-based governance, where decisions are made based on the number of tokens members hold, and delegated voting, where members delegate their voting rights to representatives. Each model impacts how governance decisions are made within the DAO. Token-based governance often leads to a more direct control structure, while delegated voting can provide more efficient decision-making by centralizing votes with trusted delegates.
How does governance token distribution influence the governance process in a Web3 project?
The governance token distribution in a Web3 project plays a key role in how decisions are made. In a token-based governance system, the voting power of each member is determined by the number of tokens they own. This means that large holders have more influence over governance decisions. The governance process allows users to vote on proposals or changes within the project, such as protocol upgrades or treasury management, directly influencing the dao’s governance.
What is the role of governance decisions within Friends with Benefits DAO (FWB DAO)?
In the Friends with Benefits DAO (FWB DAO), governance decisions are made by the dao members, who are empowered through token-based governance. Members of FWB DAO use their voting rights to influence the direction of the community, make proposals, and allocate the dao treasury. This decentralized approach allows for a governance process that reflects the values and interests of the community, making voting power an essential tool in guiding the DAO’s development.
How does the Ethereum blockchain support decentralized governance through DAO governance structures?
The Ethereum blockchain provides the foundational infrastructure for decentralized governance through DAO governance structures. These structures allow dao members to participate in decentralized voting using governance tokens, which represent voting power. DAO structures on the Ethereum blockchain ensure that decisions are not made by a central authority but are instead collectively determined by members. This ensures that governance relies on the principles of transparency, accountability, and fairness, which are key to the success of decentralized governance.