Exploring the Intricacies of Blockchain Technology Layers
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, a revolutionary paradigm has emerged, altering how we perceive and interact with data. This intricate framework, characterized by its multi-faceted approach, enables secure transactions, transparency, and immutability without the need for traditional intermediaries. The essence of this phenomenon lies in its unique architecture, which facilitates a distributed manner of recording and verifying information.
As we delve deeper into this realm, it becomes crucial to comprehend the distinct components that contribute to its overall functionality. Each segment plays a pivotal role, interacting seamlessly to create a robust environment that fosters trust and efficiency. By dissecting these individual sections, one can gain insights into not only how information is managed but also why this innovation holds immense potential across various industries.
Ultimately, a firm grasp of these intricate elements allows for better appreciation of the transformative impact on business practices and societal structures. With continuous advancements, this domain promises to redefine standards, pushing boundaries and inviting new possibilities for global connectivity and collaboration.
What Is Blockchain Technology?
This innovative framework operates as a decentralized digital ledger that securely records transactions across multiple nodes in a network. By utilizing cryptographic principles, it ensures that data remains immutable and transparent, making it an appealing solution for various applications ranging from finance to supply chain management.
The key components of such a system include distributed databases, consensus mechanisms, and smart contracts, all of which work in harmony to facilitate secure and efficient operations. Here’s a breakdown of these essential elements:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Distributed Ledger | A shared database that is replicated across multiple locations, ensuring transparency and redundancy. |
| Consensus Mechanism | A protocol that ensures all participants agree on the current state of the ledger, preventing fraud and errors. |
| Smart Contracts | Self-executing contracts with the agreement directly written into code, automating processes and reducing the need for intermediaries. |
This framework offers a promising avenue for enhancing trust and security within digital interactions, transforming how individuals and organizations conduct business in an increasingly interconnected world.
Core Components of Blockchain Systems
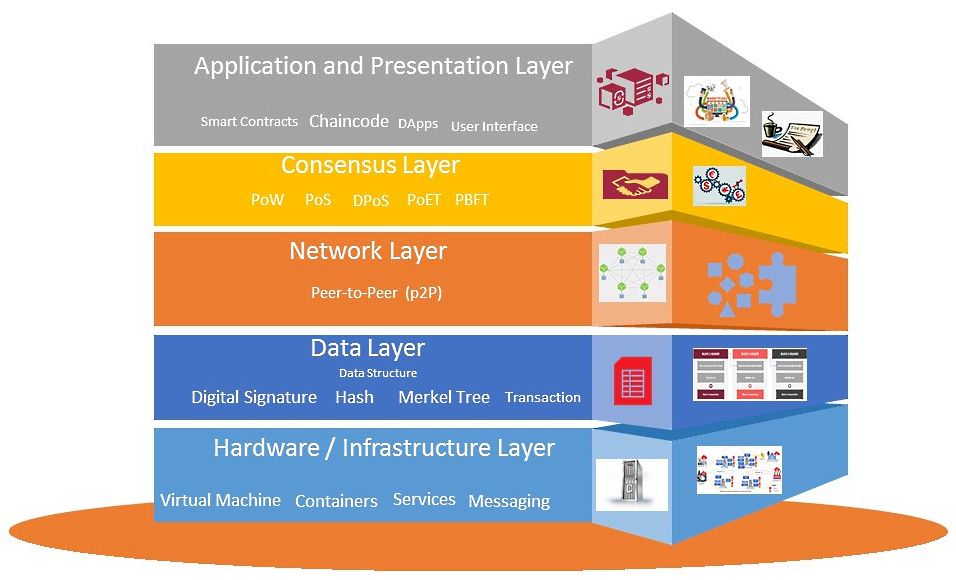
At the heart of distributed ledger frameworks lie various essential elements that function harmoniously to create a secure and efficient environment for recording transactions. These integral parts play critical roles in ensuring transparency, data integrity, and user trust. Each component contributes distinct characteristics that enable the overall functionality of the network. Blockchain is a distributed ledger that has revolutionized the way we think about data integrity and security.
Nodes in a blockchain serve as the backbone of decentralized systems, acting as individual participants in the blockchain that maintain and validate the ledger. Each node holds a copy of the entire record, ensuring redundancy and enhancing blockchain security against malicious attacks. This foundation of blockchain ensures that all transactions are recorded on the blockchain accurately and securely.
Consensus mechanisms are pivotal in achieving agreement among nodes on the validity of transactions. By utilizing methods such as proof of work or proof of stake, networks can prevent double-spending and maintain a consistent state across all nodes without the need for a central authority. These mechanisms are part of the infrastructure layer that supports the blockchain industry.
Smart contracts introduce automated processes to agreements, enabling self-executing contracts that eliminate the need for intermediaries. These programmable contracts operate on predefined conditions, enhancing efficiency and reducing potential disputes between parties. They are a key component of the implementation layer and contribute to blockchain scaling solutions.
Cryptographic techniques underpin data security within distributed ledgers. Utilizing hashing algorithms and public-private key pairs ensures that transaction details remain confidential while enabling verification of identities and data integrity. These techniques are part of the hardware infrastructure layer and are essential for blockchain security.

Finally, decentralized applications (dApps) harness the power of these fundamental components to deliver innovative services. By operating atop distributed frameworks, these applications offer enhanced resilience, transparency, and user-controlled environments. They are examples of layer 2 blockchain and layer 3 blockchain solutions, which are part of the five layers that make up the blockchain layers explained.
The layer one blockchain is responsible for the core protocol and consensus mechanisms, while layer 2 scaling solutions like layer 2 and layer 3 handle off-chain transactions to improve scalability. The layer zero includes the examples of layer 0 such as the physical infrastructure and network protocols that support the existing blockchain. The second layer focuses on blockchain scaling and includes layer 2 and layer 3 solutions that enhance the performance of the blockchain ecosystem.
In summary, the blockchain industry relies on a multi-layered approach, with each layer of the blockchain ecosystem playing a specific role. From the first layer that handles core functionalities to the layer is responsible for managing off-chain transactions, each layer contributes to the advancements in blockchain technology. The fundamentals of blockchain are built on these layers, ensuring that blockchain is a decentralized and secure system for all participants in the blockchain.
Layer includes various components such as nodes in a blockchain, smart contracts, and cryptographic techniques, all working together to provide a robust ledger technology. The example of a layer like layer 2 blockchain shows how blockchain scaling solutions can be implemented to improve the efficiency and scalability of the network. The layer one and layer two solutions, along with layer 2 and layer 3 technologies, demonstrate the continuous evolution and innovation within the blockchain industry.
How Consensus Mechanisms Work
Consensus mechanisms play a crucial role in ensuring agreement among distributed networks. They establish a reliable method for participants to validate transactions and maintain coherence within the system. This collective agreement is essential to prevent discrepancies and uphold the integrity of data shared among nodes.
At the core of these mechanisms lies a variety of algorithms designed to facilitate this process. Each algorithm has distinct characteristics, influencing factors such as speed, security, and energy consumption. For example, some protocols rely on proof-of-work, requiring participants to solve complex mathematical problems, while others utilize proof-of-stake, where the likelihood of being selected for validation is proportional to the amount staked.
The effectiveness of consensus approaches is measured by their ability to provide reliability without a central authority. This decentralization fosters trust among users, as decisions are made collectively rather than dictated by a single party. In various applications, these mechanisms ensure that transactions are processed fairly and openly, enhancing overall confidence in the system.
Ultimately, the choice of consensus method can significantly impact the performance and scalability of the network. As diverse use cases evolve, innovative consensus solutions continue to emerge, aiming to balance efficiency with unparalleled security, enabling a wide range of applications in data management and beyond.
Smart Contracts and Their Applications
Smart contracts represent a transformative innovation enabling automated agreements and transactions. They facilitate interactions between parties without intermediaries, relying on code to define conditions and execute actions. This mechanism ensures trust and efficiency, minimizing the potential for disputes and reducing the need for third-party oversight.
These programmable agreements find utility across various sectors. In finance, they enable quicker transactions and streamlined lending processes, significantly enhancing traditional models. In supply chain management, they offer enhanced transparency, tracking goods and illustrating the movement from producer to consumer.
Moreover, smart contracts are vital in real estate transactions, automating property transfers and recording ownership changes securely. The healthcare industry also benefits by safeguarding patient data while ensuring that consent and compliance procedures are adhered to seamlessly.
As adoption grows, new use cases continue to emerge, showcasing the flexibility of smart contracts in addressing complex scenarios across multiple industries. Their ability to increase efficiency and reduce costs positions them as a key component in future digital transformations.
The Role of Cryptography in Security
In the realm of digital solutions, cryptographic methods form a crucial foundation for ensuring data integrity, confidentiality, and authenticity. These sophisticated techniques safeguard information from unauthorized access, making them indispensable in various applications related to decentralized systems.
Encryption stands out as a primary mechanism employed to protect sensitive data. By transforming readable information into a coded format, it ensures that only individuals with the correct keys can decipher the content. This process is vital for maintaining privacy, especially in transactions and communication channels.
Another important aspect is hashing, which generates unique identifiers for data sets. This technique not only verifies data integrity but also enables efficient data retrieval. Even a minor alteration in the original content results in a completely different hash, indicating potential tampering.
Moreover, digital signatures provide a method to authenticate identities and confirm the origin of information. They offer a mechanism for users to prove their ownership of specific data, thereby building trust among parties engaged in exchanges.
Ultimately, these cryptographic elements work in unison, creating a fortified environment that deters fraud, enhances user trust, and supports the secure operation of decentralized networks.
Future Trends in Blockchain Development
As we look ahead, the evolution of decentralized systems promises to redefine numerous sectors, enhancing security, transparency, and efficiency. Innovations are emerging that will reform how entities interact, and foster new opportunities for collaboration and trust among participants.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Expansion
A significant trend is the surge in decentralized finance solutions. These platforms provide traditional financial services without intermediaries, allowing users to lend, borrow, and earn interest on their assets. Key features include:
- Increased accessibility to financial services
- Lower transaction fees
- Greater control over personal assets
Integration with Emerging Technologies
The synergy between various emerging technologies and decentralized systems is on the rise. The collaborative use of these innovations can lead to transformative changes:
- Artificial Intelligence: Enhancing data analysis and decision-making processes.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Creating secure and efficient communication between devices.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Ensuring end-to-end transparency and traceability.
As these trends develop, the future landscape will likely be shaped by increased interoperability, regulatory advancements, and heightened user awareness, paving the way for broader acceptance and innovative applications.
Q&A: Understanding the layers of blockchain technology
What are the main layers of blockchain technology, and how do they interact with each other?
The main layers of blockchain technology typically include the network layer, the protocol layer, the consensus layer, and the application layer. The network layer is responsible for the infrastructure that supports the blockchain, facilitating communication between nodes. The protocol layer defines the rules and standards for data exchange on the blockchain, ensuring that all participants adhere to the same set of regulations. The consensus layer establishes how transactions are confirmed and agreed upon by the network, employing various mechanisms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake. Finally, the application layer consists of the services and applications built on top of the blockchain, which utilize the functionalities of the underlying layers. Together, these layers work in harmony to create a secure and efficient blockchain ecosystem.
How does the consensus mechanism play a crucial role in blockchain layers?
The consensus mechanism is pivotal in the consensus layer of blockchain technology, as it determines how transactions are validated and added to the blockchain. This mechanism ensures that all participants in the network agree on the current state of the blockchain, thus preventing fraud and double-spending. Different types of consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work, Proof of Stake, and Delegated Proof of Stake, offer varying degrees of security, scalability, and decentralization. By ensuring that nodes reach an agreement without needing a central authority, the consensus layer maintains the integrity and reliability of the entire blockchain system, making it trustless and decentralized.
What are the potential benefits of understanding the different layers of blockchain technology?
Understanding the different layers of blockchain technology can provide numerous benefits for individuals and organizations. First, it enhances comprehension of how blockchain operates, enabling better decision-making when implementing solutions. Knowledge of each layer can aid in identifying which aspects of the technology can be leveraged to solve specific problems, such as improving security or increasing transaction speeds. Additionally, a deeper understanding can lead to more effective collaboration with developers and technical staff, fostering innovation and better product development. Ultimately, grasping the various layers of blockchain leads to more informed choices in investing, developing, and integrating blockchain solutions.
Can you explain the role of the application layer and its importance in the blockchain ecosystem?
The application layer is the topmost layer of the blockchain stack and includes all the user-facing applications and services built on the blockchain infrastructure. This layer is crucial as it translates the technological capabilities of the underlying layers into practical tools that end users can utilize. For instance, decentralized applications (dApps), smart contracts, and blockchain-based financial services operate within this layer. The importance of the application layer lies in its ability to shape user experience and drive adoption of blockchain technology. By providing accessible and intuitive applications, this layer plays a vital role in demonstrating the benefits of decentralization, transparency, and security to a broader audience, ultimately contributing to the growth of the blockchain ecosystem.
How do different blockchain architectures impact the design and development of applications?
Different blockchain architectures, such as public, private, and consortium blockchains, significantly influence the design and development of applications. Public blockchains, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, are open to anyone and prioritize decentralization and transparency, making them ideal for applications requiring trustless interactions. In contrast, private blockchains, utilized by enterprises for internal processes, focus on speed and privacy, allowing for faster transactions with permissioned access. Consortium blockchains, which are governed by a group of organizations, strike a balance between the two, often used in collaborative environments like supply chains. Understanding these architectural differences helps developers tailor their applications to meet specific needs regarding security, scalability, and performance, ultimately leading to more effective solutions in a variety of industries.
What are the different layers of blockchain technology, and how do they work together?
Blockchain technology is typically structured in layers that help facilitate its operation and applications. The most commonly discussed layers are the protocol layer, the network layer, and the application layer. The protocol layer serves as the foundational set of rules that govern how transactions are created and validated on the blockchain. The network layer is responsible for the peer-to-peer communication between nodes, ensuring that information is distributed and synchronized across the network. Finally, the application layer encompasses the various applications and services built on top of the blockchain, such as smart contracts and decentralized apps (dApps). Together, these layers create a cohesive system that allows for secure, transparent transactions without the need for intermediaries.
How do these layers enhance security and scalability in blockchain systems?
The layered architecture of blockchain technology plays a crucial role in enhancing both security and scalability. The protocol layer establishes cryptographic principles that ensure data integrity and security by using hash functions and cryptographic signatures. This means that any alteration in the data can be easily detected, thereby securing the network against tampering. The network layer contributes to security by distributing data across multiple nodes, making it difficult for malicious actors to target a single point of failure. Scalability is improved through various techniques like sharding and layer two solutions, which allow for more transactions to be processed simultaneously without burdening the main chain. By efficiently organizing these layers, blockchain can support a growing number of users and transactions while maintaining a high level of security.
What is the difference between layer 1 and layer 2 blockchains?
Layer 1 blockchains, such as bitcoin blockchain and ethereum blockchain, operate as the main blockchain and handle all transactions on the blockchain. Layer 2 solutions are built on top of layer 1 to improve blockchain scalability and reduce transaction costs by processing transactions off-chain before finalizing them on the underlying blockchain.
How does a layer 2 solution help with blockchain scalability?
A layer 2 solution helps with blockchain scalability by processing transactions off-chain or bundling multiple transactions together before recording them on layer 1 blockchains. This reduces congestion on the base layer, lowers transaction fees, and increases transaction speed, making blockchain networks more efficient.
What role does layer 0 play in the blockchain ecosystem?
Layer 0 provides the foundational layer for blockchain networks by enabling interoperability between multiple layers in blockchain technology. It facilitates communication between different blockchain platforms and ensures that blockchain developers can build scalable and interconnected blockchain solutions.
What are some examples of layer 2 blockchains?
Examples of layer 2 blockchains include the Lightning Network for the bitcoin blockchain and Optimistic Rollups for the ethereum blockchain. These scaling solutions allow faster and cheaper transactions while maintaining the security of the layer 1 blockchain.
How does layer 3 enhance blockchain functionality?
Layer 3 solutions are built on top of layer 2 and focus on application-specific use cases, such as decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, gaming, and non-fungible tokens. These solutions help interact with the blockchain more efficiently by optimizing smart contract execution and improving user experience.



