The History of ethereum Blockchain

Throughout recent years, a fascinating realm has emerged, transforming various sectors and shifting paradigms of digital interactions. This innovative phenomenon has captured the attention of technologists, investors, and enthusiasts alike, paving new paths for decentralized applications and smart contracts. As this intriguing development gained momentum, numerous milestones marked its ascent into mainstream consciousness.
Foundational elements laid the groundwork for a vibrant ecosystem, attracting a diverse group of developers and visionaries. Driven by a vision of collaborative and transparent systems, pioneers worked diligently to establish frameworks that prioritized user autonomy and data integrity. Each advancement brought forth unique challenges and opportunities, molding perception and adoption of these remarkable technologies.
In understanding its intricate progression, one uncovers stories of innovation, resilience, and ambition. Key events stand out, highlighting transformational moments that played a pivotal role in shaping this expansive landscape. As players in this arena navigated complexities, they forged connections beyond borders, fostering a communal spirit that transcended traditional limitations.
As we delve deeper into this remarkable saga, it becomes clear that experiences of individuals and communities have intertwined, creating a rich tapestry of knowledge and purpose. This exploration sheds light on dynamic interplay of technology and society, underscoring potential impacts on future endeavors. Embarking on this narrative offers a unique opportunity to grasp essence of a movement that continues to reshape our digital world.
Origins of the Ethereum Concept
At its core, this segment explores the foundational ideas and vision that sparked the creation of a decentralized platform aimed at enabling innovative decentralized applications. It delves into the motivations behind developing a flexible infrastructure capable of supporting smart contracts and enhancing peer-to-peer transactions.
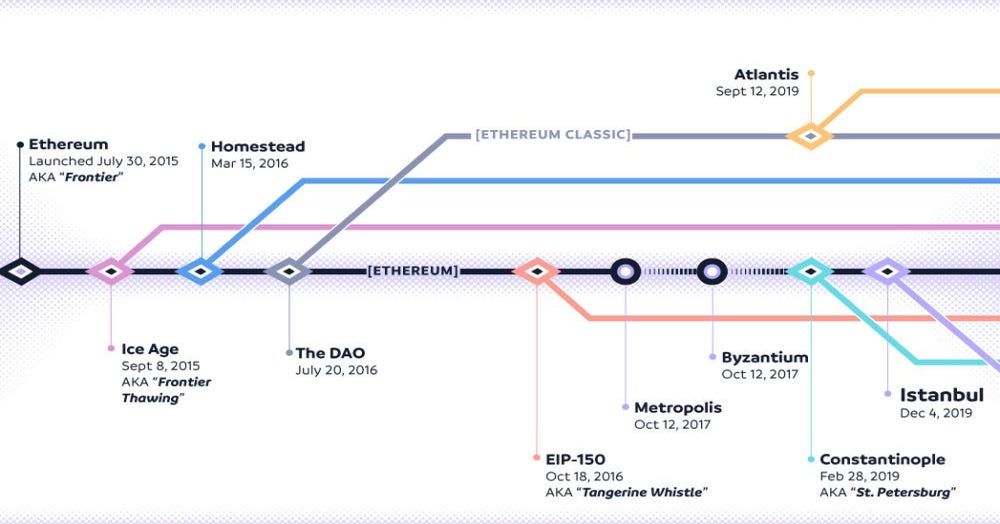
The journey began with a desire to refine existing financial systems and introduce a new paradigm where trust is embedded in code rather than relying solely on intermediaries. The visionary minds behind this initiative sought to empower individuals, allowing them to interact seamlessly without geographical constraints.
In 2013, a white paper was published by a young programmer, who proposed a system that would revolutionize digital interaction through smart contracts–self-executing agreements with terms directly written into code. This document sparked interest within a growing community of developers, enthusiasts, and investors who recognized the potential for a more open and transparent digital ecosystem.
This initial concept laid the groundwork for an extensive ecosystem where innovation could thrive beyond traditional frameworks. As initial discussions evolved, it became apparent that a new protocol was necessary, capable of supporting diverse applications across various industries. Thus began the exploration into designing a new digital environment that would challenge conventional norms and foster a future driven by automation and decentralization.
Development Milestones of Ethereum
This segment delves into significant achievements in the evolution of a leading decentralized platform, highlighting pivotal moments that shaped its progress and functionality over time. Understanding these achievements provides insights into the architecture and vision that drive its community and technology forward.
| Year | Milestone | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2013 | White Paper Release | A conceptual framework was introduced by Vitalik Buterin, presenting foundational ideas for smart contracts and decentralized applications. |
| 2015 | Genesis Block | The initial block was mined, marking official launch and activation of the network, allowing users to create and deploy smart contracts. |
| 2016 | DAO Incident | A pioneering decentralized autonomous organization faced a critical exploit, leading to significant discussions on governance and security. |
| 2017 | Network Upgrade (Metropolis: Byzantium) | Enhancements in scalability, privacy features, and developer tools were implemented, improving overall efficiency. |
| 2020 | Ethereum 2.0 Beacon Chain | Launch of a new proof-of-stake chain, laying groundwork for transition to a more sustainable and scalable version of the platform. |
| 2021 | Smart Contract Adoption | Increased usage of smart contracts across various sectors, including finance and art, leading to a surge in decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs). |
| 2022 | Merge | A significant event merging the original chain with the proof-of-stake chain, drastically reducing energy consumption and enhancing network security. |
Key Innovations and Features Introduced
This section explores significant advancements and characteristics that have emerged, shaping the landscape of decentralized applications and digital assets. These groundbreaking contributions have not only enhanced functionality but also expanded use cases, setting a new standard for future developments in distributed technology.
Smart Contracts
One of the most pivotal innovations involves programmable agreements that execute automatically when predetermined conditions are met. This feature allows developers to create decentralized applications with diverse functionalities, streamlining processes across various sectors such as finance, supply chain, and governance.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
A transformative movement has taken root, enabling users to engage in financial activities without traditional intermediaries. This ecosystem empowers individuals with greater control over their assets, offering innovative financial instruments like lending, borrowing, and yield farming, thus democratizing access to financial services worldwide.
Challenges Faced During Network Expansion
As a decentralized platform grew in popularity, numerous obstacles emerged that threatened its stability and performance. The rapid influx of users and transactions spurred a series of technical and operational hurdles that demanded innovative solutions. Addressing these challenges became essential for maintaining user trust and ensuring seamless interactions within the network.

Scalability Issues
One of the primary difficulties encountered was scalability. As more participants engaged with the system, the demand for processing power and storage increased tremendously. This led to slower transaction times and higher fees, which in turn hindered user experience. Finding a balance between decentralization and speed presented a significant challenge for developers.
Security Concerns
Alongside scalability, security became a prominent issue. With increased activity, the risk of malicious attacks and vulnerabilities also surged. Protecting personal data and ensuring transaction integrity required continuous vigilance and updates to security protocols. Developers worked tirelessly to fortify defenses and minimize risks for users.
| Challenge | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | Increased demand for transactions and data processing | Slower speeds, higher fees |
| Security | Rise in malicious attacks and vulnerabilities | Potential data breaches, loss of trust |
| Interoperability | Connecting with other platforms and systems | Limited functionality, fragmented ecosystem |
Impact of the DAO Incident
This event marked a significant turning point, raising crucial questions about security, governance, and trust within decentralized systems. The fallout not only revealed vulnerabilities but also prompted a reevaluation of protocols and mechanisms employed in such environments. As a result, this incident has had lasting implications on how digital assets and communities operate.
Security Vulnerabilities Exposed
One of the most apparent consequences was the unveiling of critical weaknesses in smart contract design. Developers and investors became acutely aware that inadequate testing and oversight could lead to devastating financial losses. Consequently, this incident spurred a wave of innovation aimed at improving security measures and best practices within code deployment.
Ecosystem Governance Transformation
The fallout from the incident also catalyzed discussions surrounding governance frameworks. Communities began to explore more robust decision-making processes and mechanisms for accountability. New models emerged that emphasized transparency and distributed authority, ultimately shaping the operational philosophies of many projects that followed.
The Future of Ethereum Evolution
Emerging technologies continually reshape landscapes, bringing forth opportunities and challenges. This transformative process involves adapting to new paradigms and enhancing functionality while maintaining core principles. Anticipation of future developments inspires innovation and collaboration across diverse sectors.
Scalability remains a focal point for upcoming advancements, as networks seek to accommodate growing user bases and transaction volumes. Enhanced mechanisms aim to optimize resource utilization and bolster throughput, ensuring seamless experiences for participants.
Security will further evolve, addressing vulnerabilities while fostering trust among users. Robust protocols and comprehensive audits will play pivotal roles in safeguarding assets and information, enabling continued participation without fear of compromise.
A collaborative ecosystem is likely to flourish, integrating various platforms and fostering interoperability. This synergy may facilitate the exchange of assets and information across differing systems, enriching the overall experience for all stakeholders involved.
As environmental sustainability gains prominence, innovative solutions focused on reducing energy consumption are expected. Eco-friendly alternatives will be prioritized, promoting not only technological progression but also responsibility towards the planet.

In essence, an exciting landscape awaits, driven by collaboration, security enhancements, sustainable practices, and the quest for efficiency. The future promises a dynamic environment where innovation thrives and diverse communities connect harmoniously.
Q&A: History of Ethereum blockchain
What is Ethereum and how did it start?
Ethereum is a decentralized, open-source blockchain system that features smart contract functionality. It was proposed in late 2013 by programmer Vitalik Buterin and development was crowdfunded in 2014, leading to the Ethereum network’s launch in July 2015. Unlike Bitcoin, which is primarily a cryptocurrency, Ethereum also serves as a platform for decentralized applications (dApps) and has its own currency called Ether (ETH). The vision was to create a blockchain that allowed developers to build and deploy smart contracts, which are self-executing agreements with the terms of the contract directly written into code.
What are some significant milestones in the Ethereum blockchain’s history?
Several key milestones mark the Ethereum blockchain’s journey. It began with the launch of the Ethereum mainnet in July 2015, followed by the successful crowdsale that raised over $18 million, one of the largest in history at that time. In 2016, Ethereum faced a major challenge with the DAO hack, which led to a hard fork and the creation of Ethereum Classic (ETC). Subsequent upgrades such as Metropolis: Byzantium in 2017 and Metropolis: Constantinople in 2019 improved scalability and privacy. The transition to Ethereum 2.0, aimed at enhancing network efficiency via proof-of-stake, has been a significant focus for developers and the community since 2020, culminating in the Beacon Chain launch in December 2020.
How do smart contracts work on the Ethereum blockchain?
Smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain are self-executing contracts with the agreement directly written into code. They run on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), which processes and executes the contract’s code when certain conditions are met. This allows for automated execution without the need for intermediaries, increasing efficiency while reducing costs. Developers write smart contracts in Solidity, a programming language designed specifically for this purpose. Once deployed, these contracts are immutable and cannot be altered, ensuring transparency and security within transactions facilitated by the Ethereum network.
What challenges has Ethereum faced throughout its development?
Ethereum has faced numerous challenges throughout its history. Initially, its scalability was a major issue, as the original proof-of-work consensus mechanism led to slow transaction speeds and high fees during periods of high demand. This culminated in the congestion seen in late 2017 with the rise of ICOs and dApps, prompting the need for scaling solutions. The DAO hack in 2016 posed existential questions about governance and security, leading to the controversial hard fork that created Ethereum Classic. More recently, the transition to Ethereum 2.0 has been complex, facing delays and uncertainty, as the network aims to move from proof-of-work to proof-of-stake to improve sustainability and scalability.
What is the future outlook for Ethereum?
The future of Ethereum appears promising as it aims to solidify its position as the leading platform for decentralized applications and smart contracts. With the ongoing rollout of Ethereum 2.0, the network aims to enhance scalability, security, and energy efficiency through the proof-of-stake mechanism. Continued developments in Layer 2 solutions, such as rollups, are expected to significantly increase transaction throughput. Growing interest from institutional investors, alongside the increasing adoption of decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs), further bolsters Ethereum’s potential. However, it also faces competition from other blockchain platforms and regulatory scrutiny that could impact its growth trajectory.
What is a short history of Ethereum and how was it founded?
Ethereum was first described in late 2013 by Vitalik Buterin, one of its co-founders, and officially launched in 2015 by the Ethereum Foundation. The platform was created to expand blockchain technology’s capabilities beyond cryptocurrency, introducing smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps) to the blockchain industry.
What are the key differences between Ethereum and Ethereum Classic?
Ethereum and Ethereum Classic diverged after a major incident in Ethereum’s history known as “The DAO Hack” in 2016. The majority of the Ethereum community supported a hard fork to reverse the hack, creating the current Ethereum blockchain. Ethereum Classic, however, maintained the original version of the Ethereum blockchain to preserve its immutability.
How does Ethereum allow developers to build decentralized applications?
Ethereum allows developers to create decentralized applications (dApps) using its smart contract functionality. These smart contracts are self-executing agreements coded directly onto the blockchain. The Ethereum platform supports various use cases, from finance to supply chain management, making it a cornerstone of the blockchain industry.
What is the role of the Ethereum Foundation and the Ethereum Improvement Proposals process?
The Ethereum Foundation is a nonprofit organization that supports the development and growth of the Ethereum project. It oversees initiatives like Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs), which are community-driven proposals for upgrades to the Ethereum protocol. These proposals help guide Ethereum’s evolution and maintain its position as a leading public blockchain.
What was the Ethereum Merge, and how did it impact the Ethereum protocol?
The Ethereum Merge was a major upgrade that transitioned Ethereum from a proof-of-work (PoW) to a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. This change significantly reduced Ethereum’s energy consumption and improved scalability, marking a pivotal moment in Ethereum’s history as it moved closer to its vision of becoming a more sustainable and efficient blockchain network.


