Understanding Layer 3 Blockchains and Their Functionality
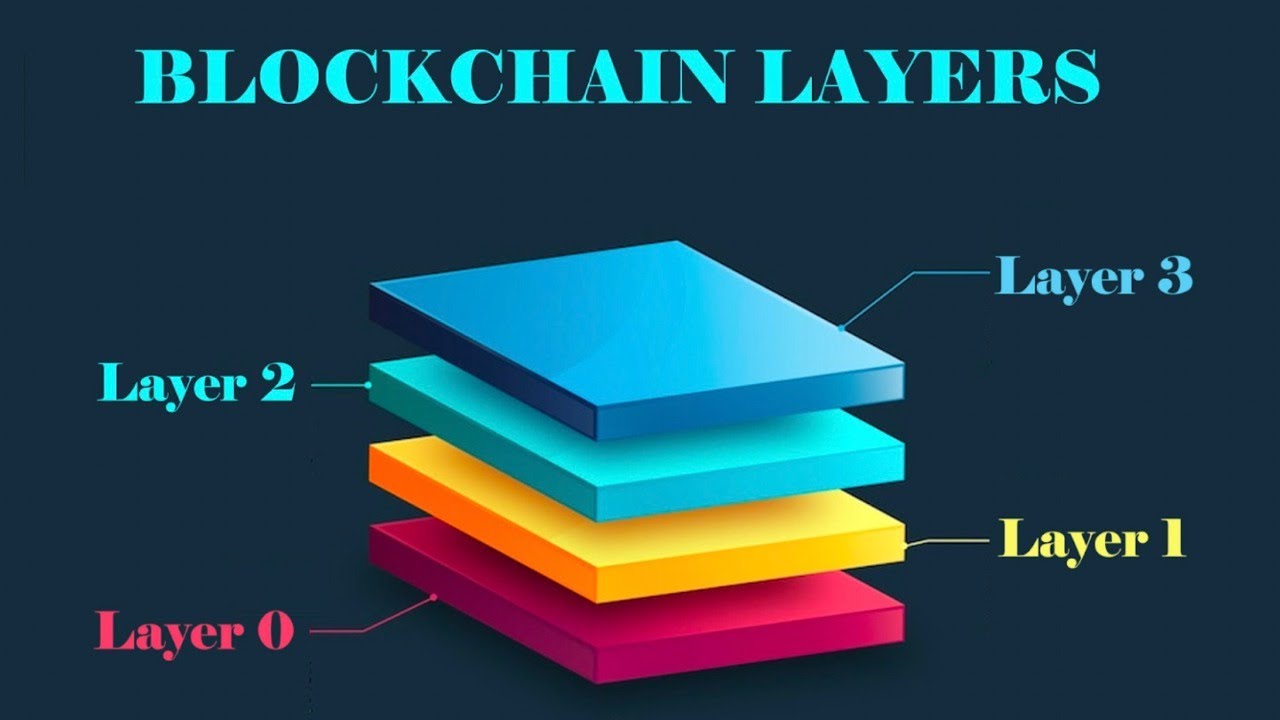
The evolution of decentralized systems has brought about innovative architectures that enhance the efficiency and usability of digital transactions. These sophisticated frameworks are designed to address challenges faced by earlier generations, paving the way for a more robust ecosystem. By delving into the components and interactions within these advanced systems, one can appreciate the significance of their roles in improving performance and scalability.
Within these intricate networks lies a crucial layer that facilitates seamless communication and data exchange among participants. This segment acts as a bridge, ensuring that transactions are executed swiftly and securely, while also accommodating a variety of applications and services. As a result, users benefit from increased accessibility, allowing them to engage with digital assets in a more meaningful way.
Furthermore, the deployment of such advanced structures supports a diverse range of functionalities, enabling developers to innovate and create customized solutions tailored to specific needs. This flexibility not only fuels creativity but also fosters a collaborative environment where new ideas can flourish, ultimately contributing to the growth and success of the entire ecosystem.
What is Layer 3 Blockchain?
The evolution of decentralized networks has led to the emergence of advanced structures that enhance the effectiveness of existing frameworks. Among these innovations, the third tier plays a crucial role in optimizing interactions and improving user experiences within digital ecosystems. This segment delves into the characteristics and significance of this cutting-edge layer.
Characteristics of the Third Tier
- Enhanced Interoperability: Facilitates communication between multiple networks, allowing seamless data exchange.
- Scalability Solutions: Introduces mechanisms to increase transaction throughput beyond traditional limits, thus accommodating growing demand.
- User-Centric Applications: Promotes the development of customized solutions tailored to specific user needs, making systems more intuitive.
Importance of the Third Tier
- Reduced Latency: Minimizes delays in transaction processing, fostering quicker verification and confirmation.
- Cost Efficiency: Lowers transaction fees by utilizing innovative techniques that streamline operations.
- Broader Accessibility: Expands the availability of services to a wider audience, making advanced technologies inclusive.
In conclusion, the third tier represents a vital advancement in the architecture of distributed networks, enhancing both performance and user engagement in the evolving digital landscape.
Key Features of Layer 3 Technology
The third layer of distributed ledger solutions introduces a suite of attributes aimed at enhancing user experience and optimizing performance. These characteristics are crucial for expanding the functionality of existing architectures, facilitating more sophisticated applications and services. By building on previous layers, this level brings forth innovations that cater to the evolving needs of developers and end-users alike.
Scalability
One of the most significant advantages of this technology is its ability to scale efficiently. It offers a means to process a higher volume of transactions without compromising speed or security, addressing one of the main challenges faced by earlier frameworks.
Interoperability
This level ensures seamless interaction among various networks and protocols, fostering a more connected ecosystem. This feature enables users to engage with multiple platforms without requiring complex conversions or adaptations.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Scalability | Enhances transaction processing capacity, allowing for greater throughput. |
| Interoperability | Facilitates communication and operation across different networks and systems. |
| User-Centric Design | Focuses on improving user experience by simplifying interactions. |
| Customizable Solutions | Allows developers to create tailored applications that meet specific market demands. |
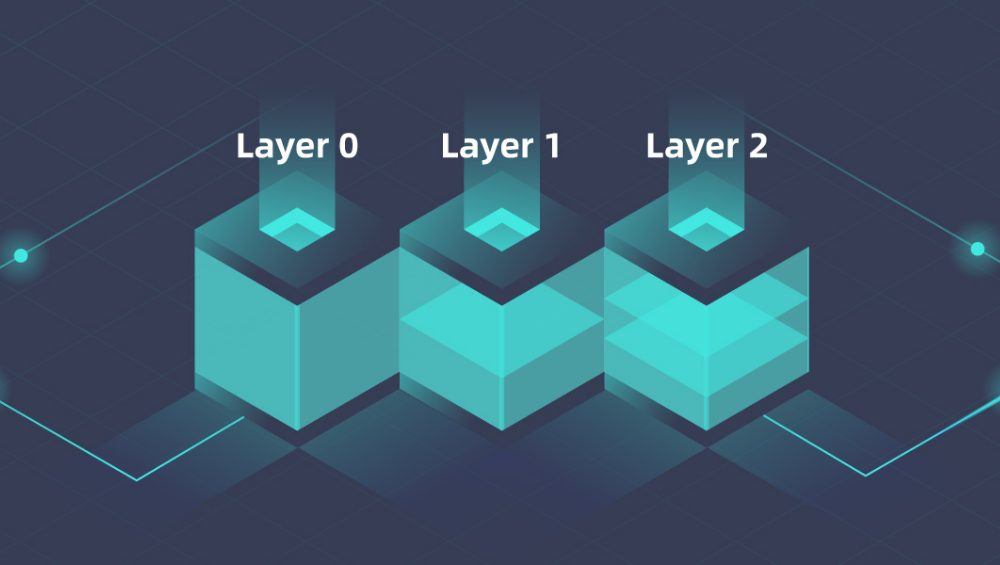
Comparison with Layer 1 and Layer 2
The various tiers of distributed networks each play distinct roles in facilitating transactions and enhancing performance. While the first tier focuses on providing the base of operations, the second tier aims to address scalability and speed. The third tier introduces innovative solutions that build upon the groundwork laid by its predecessors, streamlining processes and offering advanced capabilities.
Characteristics of the First Tier
The foundational tier serves as the primary network protocol, where transaction verification and consensus mechanisms occur. It boasts robustness and security, making it a reliable option for executing operations but often faces challenges in terms of speed and transaction costs. This layer can become congested during high activity periods, resulting in delays and increased fees.
Role of the Second Tier
In contrast, the secondary level essentializes efficiency by creating a framework for quicker transactions and lower costs. Through techniques such as state channels or sidechains, this tier aims to alleviate the burden on the primary network. Although it enhances user experience, it may sacrifice some degree of decentralization and security typical of the base level. By offloading some transactions, it allows more room for processing on the foundational layer.
In summary, while the primary tier underpins the entire structure and the secondary tier develops speed and affordability, the third tier seeks to innovate further by enabling complex functionalities that go beyond traditional capabilities. Each tier offers unique advantages and considerations, ultimately contributing to the evolution of the technology landscape.
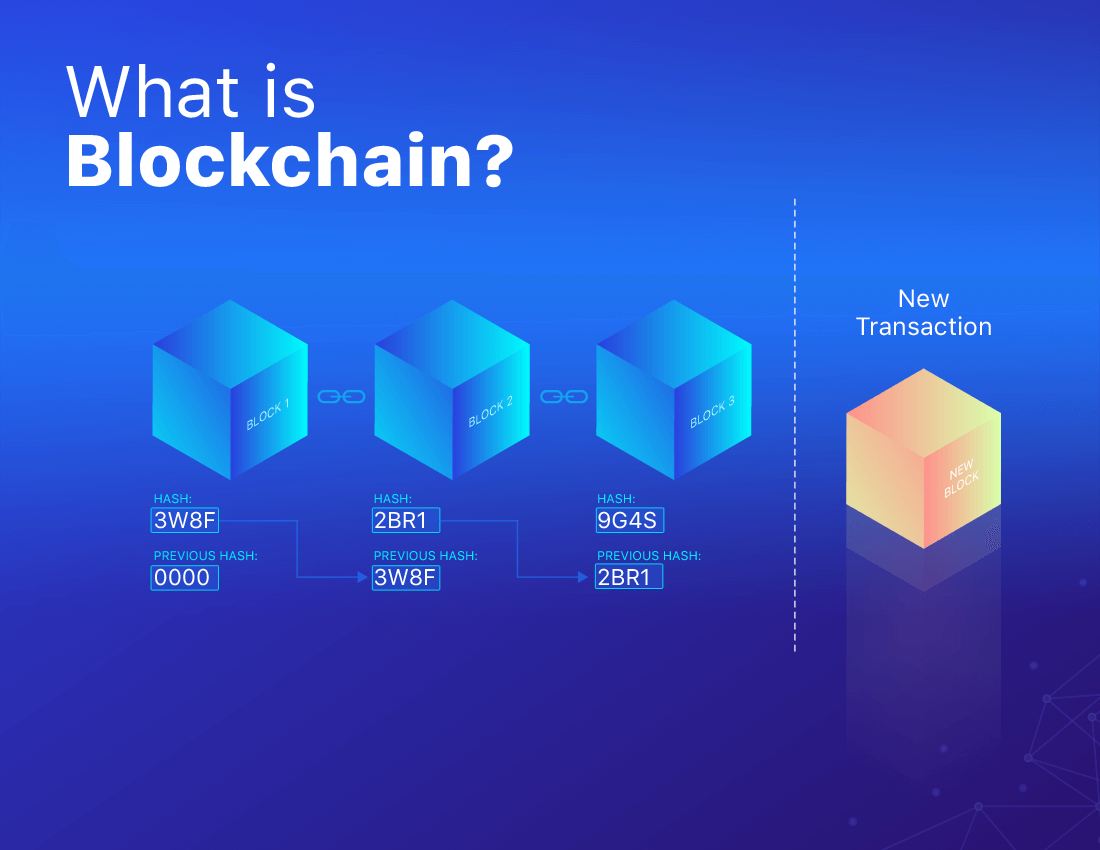
Real-World Applications and Use Cases
Innovative technologies are increasingly finding their way into various sectors, creating opportunities for enhanced transparency, efficiency, and security. The integration of decentralized systems into everyday processes is transforming industries, enabling new solutions to age-old challenges.
Finance and Payments
In the financial sector, decentralized networks offer a faster and more efficient way to conduct transactions. By removing intermediaries, users can send and receive funds in real-time with reduced fees. For example, cross-border payments are becoming more streamlined, allowing individuals and businesses to transact globally with minimal delays. Furthermore, these networks provide avenues for creating digital assets, such as stablecoins, which offer stable value and can be used for everyday purchases.
Supply Chain Management
Another notable application lies in supply chain operations. The ability to trace products from their origin to the end consumer enhances accountability and reduces fraud. Companies can utilize decentralized ledgers to monitor the journey of goods, ensuring transparency at every stage. This visibility not only improves trust among consumers but also facilitates better inventory management and reduces losses.
Moreover, retailers can quickly verify the authenticity of products, combat counterfeit goods, and enhance their overall brand reputation. As a result, many organizations are now exploring how to integrate these advanced solutions into their existing frameworks.
Challenges Facing Layer 3 Solutions
The emergence of advanced architectures has brought a myriad of opportunities, yet it has also introduced a set of challenges that developers and users alike must navigate. As innovations flourish, understanding the hurdles that come with implementing these systems becomes crucial for their future evolution and adoption.
Technical Complexities
One of the primary obstacles encountered involves the intricate nature of development. Creating efficient protocols often requires extensive knowledge and experience. This complexity can lead to increased development times and potential security vulnerabilities. Balancing performance and scalability is a critical aspect that needs to be meticulously handled to avoid pitfalls that could undermine the system’s reliability.
User Adoption Issues
Beyond technical hurdles, gaining traction among users poses another significant challenge. Education and awareness play essential roles in facilitating adoption. Many potential users may feel overwhelmed by new concepts and terminologies, which can deter engagement. Additionally, existing solutions may create a sense of comfort, making it difficult for innovative approaches to establish themselves in a competitive marketplace.
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Technical Complexities | Development requires advanced skills, leading to potential delays and security issues. |
| User Adoption Issues | Overcoming ignorance and inertia is needed to encourage widespread use. |
The Future of Layer 3 Innovations
The advancement of decentralized networks is poised to pave new avenues for technological expansion and user experience. With the continuous evolution of protocols designed for scalability, the next generation promises seamless interactions and enhanced capabilities that will cater to both developers and end-users.

Emerging trends in this space indicate a shift towards:
- Interoperability: As systems become more complex, the ability to communicate across various protocols will be critical. Future innovations may focus on creating bridges that facilitate smoother interactions.
- Enhanced Security: With increasing concerns about data breaches, the development of advanced security measures will likely be a priority, ensuring that transactions and user privacy remain protected.
- Customized Experiences: Future solutions may allow users to tailor their experiences, providing flexibility in managing applications according to personal preferences.
- Decentralized Applications (dApps): There will be a continued rise in user-friendly dApps, making technology more accessible to the general population while retaining robust performance.
As we look to the horizon, innovations in this realm are expected to drive significant advancements in efficiency and accessibility, ultimately revolutionizing the digital landscape for individuals and enterprises alike.
Q&A: Layer 3 Blockchain: How It Works
What is a Layer 3 blockchain and how does it differ from Layer 1 and Layer 2?
A Layer 3 blockchain is an abstraction layer built on top of Layer 1 and Layer 2 blockchains to enhance application functionalities and interoperability. While Layer 1 refers to the base blockchain (like Bitcoin or Ethereum) where transactions are processed and recorded, Layer 2 consists of solutions like sidechains or state channels that focus on scalability and transaction speed. Layer 3, in contrast, is primarily focused on providing a seamless user interface, cross-chain compatibility, and application-specific features. It allows developers to build decentralized applications (dApps) that can interact with multiple blockchains, improving usability and functionality for end users.
What are some advantages of using Layer 3 solutions in blockchain applications?
Layer 3 solutions offer several advantages for blockchain applications. Firstly, they provide enhanced interoperability, enabling dApps to interact with different blockchains seamlessly. This interconnectivity allows for more comprehensive functionalities and user experiences. Secondly, Layer 3 can drastically improve user interfaces, making blockchain applications more user-friendly and accessible to non-technical users. Thirdly, by offloading certain functions to Layer 3, it helps ease congestion on Layer 1 and Layer 2 solutions, enhancing overall system performance. Lastly, Layer 3 can introduce application-specific features and optimizations tailored to the needs of particular user groups or industries, thus broadening application use cases.
Can you explain how Layer 3 can improve scalability and performance for blockchain networks?
Layer 3 improves scalability and performance by offloading specific tasks from the underlying blockchains. By handling functions like transaction validation, data storage, and user interactions at this higher layer, Layer 3 can reduce the workload on Layer 1 and Layer 2, which are often limited by their inherent capacities. For example, a Layer 3 protocol can implement more efficient data management practices or employ DApps that bundle transactions, allowing more users to engage without putting pressure on the core network. This architectural approach not only enhances the overall throughput of the network but also minimizes latency, ultimately resulting in faster transaction times and a more responsive blockchain experience for users.
What role do Layer 3 blockchains play in enhancing user experience in decentralized applications?
Layer 3 blockchains play a crucial role in enhancing user experience in decentralized applications (dApps) by focusing on interface improvements, user-friendly design, and tailored functionalities. Since many users find blockchain technology complex, Layer 3 can abstract away the technical complexities, offering intuitive interfaces that resemble traditional applications. This way, users can navigate dApps without needing extensive knowledge of blockchain principles. Furthermore, Layer 3 allows for features like wallet integration, seamless cross-chain transactions, and easy onboarding processes. These enhancements can significantly lower the entry barrier for new users, making decentralized technologies more accessible and appealing.
Are there any notable examples of Layer 3 solutions currently in use?
Yes, several notable Layer 3 solutions are currently making waves in the blockchain ecosystem. One prominent example is the Optimism protocol, which enhances Ethereum functionality by focusing on reducing transaction costs and increasing speed through optimistic rollups, a technology that allows multiple transactions to be bundled and settled on Layer 1 in a single operation. Another example is the Polygon network, offering various tools and frameworks for developers to build Layer 2 and Layer 3 solutions, thus improving user experiences across multiple Ethereum dApps. Lastly, Layer 3 frameworks like Arweave and Filecoin are being used for data storage and retrieval, showcasing the versatility of Layer 3 in addressing diverse blockchain application requirements.
What is a layer 1 blockchain, and how does it differ from other blockchain layers?
A layer 1 blockchain refers to the base layer of a blockchain protocol, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. It is the foundational blockchain architecture that validates and records transactions without relying on other blockchain systems. In contrast, layer 2 solutions and layer 3 applications are built on top of layer 1 blockchains to improve scalability, interoperability, or provide specialized functionalities.
How do layer 2 scaling solutions address the blockchain scalability issue?
Layer 2 scaling solutions are designed to reduce the load on the main blockchain by processing transactions off-chain or in parallel to the underlying blockchain. These layer 2 networks, such as rollups or state channels, help enhance transaction throughput and reduce costs while maintaining the security and decentralization of the base layer.
What is the blockchain trilemma, and how do blockchain scaling solutions aim to resolve it?
The blockchain trilemma refers to the challenge of balancing scalability, decentralization, and security within blockchain systems. Blockchain scaling solutions, including layer 2 protocols and layer 3 projects, aim to address this by improving the scalability of various blockchain networks without compromising the security or decentralization of the underlying blockchain.
What is the role of layer 3 in the blockchain space, and how do layer 3s work?
Layer 3 in the blockchain space is often referred to as the application layer. Layer 3 solutions aim to provide user-facing services such as decentralized applications (dApps) or cross-chain interoperability. These solutions work on top of layer 2 networks or directly interact with existing layer 1 and layer 2 protocols to enable seamless functionality across multiple blockchain networks.
How does the development of layer 2 solutions enhance the evolution of blockchain technology?
The development of layer 2 solutions enhances the evolution of blockchain technology by addressing the scalability issue that hinders many existing blockchain platforms. These layer 2 scaling solutions enable higher transaction throughput, lower fees, and increased efficiency, facilitating the growth of blockchain projects and the broader crypto industry while maintaining the core principles of decentralization and security.





