Understanding the Distinction Between Web3 and Web 3.0 – Web3 is not same as web 3.0

In recent years, conversations surrounding online innovations have taken on heightened significance. New frameworks emerge to shape how individuals interact in digital landscapes, each presenting unique features and functionalities. These advancements aim to redefine connections, transactions, and user experiences in a way that transcends prior conventions.
A nuanced examination reveals various interpretations and implications tied to these innovative concepts. Each term embodies distinct philosophies and technologies, reflecting broader shifts in how we envision online ecosystems. A deeper look unveils layers of complexity that merit consideration, influencing both developers’ approaches and users’ engagements.
As ongoing developments reshape the digital terrain, it becomes essential to parse out these evolving concepts. The interplay of decentralization, user sovereignty, and enriched interactivity forms a pivotal axis around which discussions revolve. By delving into their distinctive aspects, one can appreciate the broader narrative of technological transformation.
Defining Web3: Key Characteristics
The evolution of online interactions has given rise to a new paradigm characterized by decentralized principles, enhanced user agency, and innovative technologies. This shift represents a departure from traditional models, emphasizing community-driven governance and trustless ecosystems. As this framework develops, several defining traits emerge that encapsulate its essence and operational framework.

Decentralization
One of the most pivotal attributes of this new landscape is decentralization. Unlike centralized systems that rely on a single authority, this approach distributes control across numerous participants. This results in a more resilient network where users share power, reducing the risk of censorship and fostering inclusivity.
User Empowerment
User empowerment serves as a cornerstone of this transformative environment. Individuals gain greater ownership of their data, identities, and digital assets. This shift enables participants to engage in transactions and communications without intermediaries, enhancing privacy and transparency in all interactions.
Exploring the Concept of Web 3.0
In recent years, digital landscapes have undergone significant transformations, prompting discussions around advanced internet paradigms. This novel approach seeks to redefine user experiences and interactions online, fostering a more decentralized environment where control and ownership shift towards individuals.
Key elements of this emerging vision include:
- Decentralization: Moving away from centralized authorities, allowing users to maintain control over their data and digital identities.
- Interoperability: Enabling seamless communication and data exchange across different platforms and services, enhancing user convenience.
- User Empowerment: Prioritizing individual agency and participation in shaping online spaces through community-driven initiatives.
- Smart Technologies: Integrating advanced algorithms and automation to create responsive and efficient systems tailored to user needs.
This paradigm promotes a shift in how individuals engage with online services, fostering collaboration, trust, and unprecedented opportunities for innovation.
As this concept evolves, it has the potential to redefine interactions, offering a more human-centered approach to technology while addressing current limitations found in existing digital frameworks.
Technological Foundations of Web3
The new era of internet architecture introduces innovative paradigms that revolutionize user interaction, data ownership, and platform dynamics. At its core, this evolution is driven by a set of technologies that empower decentralized applications and enhance user experiences. By leveraging advancements in various fields, this paradigm aims to create a more transparent, secure, and user-centric environment.
Blockchain technology serves as a cornerstone of this movement, offering a distributed ledger that ensures accountability and transparency. This decentralized framework enables secure transactions without the need for traditional intermediaries, fostering trust among users. Additionally, the use of smart contracts automates processes and enforces agreements without manual intervention, enhancing efficiency and reducing the potential for disputes.
Another significant component comes from Decentralized Finance (DeFi), which challenges conventional financial systems by providing users with direct access to financial services without relying on centralized institutions. This shift not only democratizes financial opportunities but also encourages innovation in how individuals manage their assets.
Tokenization plays a vital role in this landscape, allowing for the representation of ownership or access to digital assets on the blockchain. This process facilitates fractional ownership and enhances liquidity, broadening the opportunities for participation across various sectors. The emergence of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) further exemplifies this trend, enabling unique digital items to be bought, sold, or traded in ways previously unimagined.
The integration of decentralized identity solutions enhances user autonomy and privacy. By allowing individuals to control their personal information, these solutions mitigate the risks associated with data breaches and misuse. Users can engage in online activities without surrendering unnecessary personal details, fostering a safer digital environment.
Ultimately, the convergence of these technologies paints a picture of a new digital frontier where users reclaim control, engage more meaningfully, and interact in a landscape designed for collaborative growth and innovation.
Philosophical Aspects of Web 3.0
The evolution of digital landscapes prompts deeper reflections on human interaction with technology. This new era invites contemplation about fundamental principles guiding digital communication, ownership, and collaboration. Philosophical inquiries into these themes reveal significant shifts in societal values and individual perspectives.
- Decentralization: Emphasizing autonomy, the shift away from central authorities raises questions about power distribution and control.
- Ownership: Concepts of digital property evolve, challenging traditional notions of possession and rights in virtual spaces.
- Trust: Mechanisms enabling trust without intermediaries invite discussions on reliability, accountability, and transparency.
- Identity: Anonymity and self-sovereignty reshape perceptions of personal identity within online environments.
Exploring these dimensions encourages a critical examination of how technological advancements impact human relationships, ethics, and social constructs. As individuals engage with these evolving concepts, a reevaluation of their roles in digital ecosystems becomes essential.
Use Cases and Applications of Web3
Innovative technologies are reshaping digital interactions, offering numerous possibilities that extend far beyond traditional internet experiences. This new paradigm enables users to engage in decentralized applications, enhancing transparency, security, and user control. Various sectors are actively exploring these opportunities, leading to exciting potential across multiple domains.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi represents a significant shift from conventional banking systems, allowing individuals to manage financial assets without intermediaries. Users can lend, borrow, and trade assets seamlessly through smart contracts, improving access to financial services for unbanked populations. With its increased transparency and lower costs, decentralized finance is emerging as a compelling alternative to traditional finance.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
NFTs have revolutionized the art and entertainment industries by creating unique digital ownership experiences. Artists and creators can tokenize their works, allowing them to retain control over their intellectual property while monetizing their creations directly. This innovative approach fosters new connections between artists and fans, opening avenues for collaboration and direct revenue generation.
Future Implications of Both Models
The evolution of internet paradigms promises to reshape our interactions, economies, and societies. As these two promising frameworks develop, it is crucial to consider their potential impacts on various sectors, including technology, finance, and social dynamics. The trajectory ahead may be influenced by the degree of decentralization, user autonomy, and data privacy that emerges from each approach.
Technological Advancements
Each framework offers unique technological innovations that could redefine how users interact with digital systems:
- Increased interoperability across platforms, fostering seamless user experiences.
- Enhanced security features, promoting trust through decentralized systems.
- Adoption of smart contracts, automating processes and reducing reliance on intermediaries.
Economic Transformations
The implications for economic structures are profound, potentially leading to a democratization of digital assets and participation:
- Creation of new financial models, enabling direct transactions without central authorities.
- Opportunities for creators to monetize their work independently, disrupting traditional revenue streams.
- Decentralized finance systems that allow access to global markets for underserved populations.
As these advancements unfold, ongoing discussions and collaborations among stakeholders will shape the outcomes and ensure that benefits are maximized while minimizing risks associated with each framework.
Q&A: Web3 is not same as web 3.0
What is the primary difference between Web3 and Web 3.0?
The primary difference lies in their core philosophies and functionalities. Web3 refers to a decentralized internet framework that emphasizes user sovereignty, privacy, and blockchain technologies to create more open and user-governed platforms. It aims to remove reliance on centralized entities, fostering peer-to-peer interactions. In contrast, Web 3.0, often associated with the semantic web, focuses on enhancing the internet’s ability to understand and process information intelligently. It aims to provide personalized user experiences through advanced AI, machine learning, and data interoperability, acting more like an intelligent layer on top of the existing web. Essentially, while both concepts strive for a better internet experience, Web3 is centered around decentralization, and Web 3.0 revolves around the intelligent processing of data.
How do Web3 technologies benefit users compared to traditional web paradigms?
Web3 technologies are designed to empower users in several significant ways. First, by utilizing decentralized networks and blockchain technology, users have greater control over their data, essentially owning it rather than allowing centralized companies to monetize it. This leads to enhanced privacy and security, reducing the risk of data breaches and misuse by third parties. Secondly, Web3 promotes transparency since transactions and interactions are recorded on public blockchains, enabling users to verify the integrity of operations without needing a central authority. Lastly, Web3 fosters community-driven development and governance through decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), allowing users to have a say in platform decisions and share in its economic success, fundamentally reshaping the relationship between users and digital services.
Will Web3 technologies completely replace traditional web services?
While Web3 technologies present revolutionary changes in how we interact with the internet, it is unlikely they will completely replace traditional web services in the near future. Instead, we may see an integration of Web3 principles into existing services, creating a hybrid model that combines the best features of both worlds. Traditional platforms may adopt decentralized elements to enhance user control and security or leverage AI and machine learning from Web 3.0 for better user experiences. Moreover, regulatory, technical, and user adoption challenges must be addressed before Web3 can gain widespread acceptance. Therefore, while Web3 will transform the digital landscape, it will coexist with traditional web services for a considerable time.
What role do cryptocurrencies play in the Web3 ecosystem?
Cryptocurrencies play a pivotal role in the Web3 ecosystem as they serve multiple essential functions. First and foremost, they act as a medium of exchange, enabling peer-to-peer transactions within decentralized applications (dApps) without needing intermediaries. This fosters a more efficient and cost-effective environment for users. Furthermore, cryptocurrencies often form the basis for governance tokens, allowing users to participate in decision-making processes for projects and platforms. Additionally, they can incentivize user engagement by rewarding participation and contributions within ecosystems, such as staking rewards or liquidity mining. In essence, cryptocurrencies not only facilitate transactions but also promote community involvement and the sustainability of decentralized networks, making them fundamental to the growth of Web3.
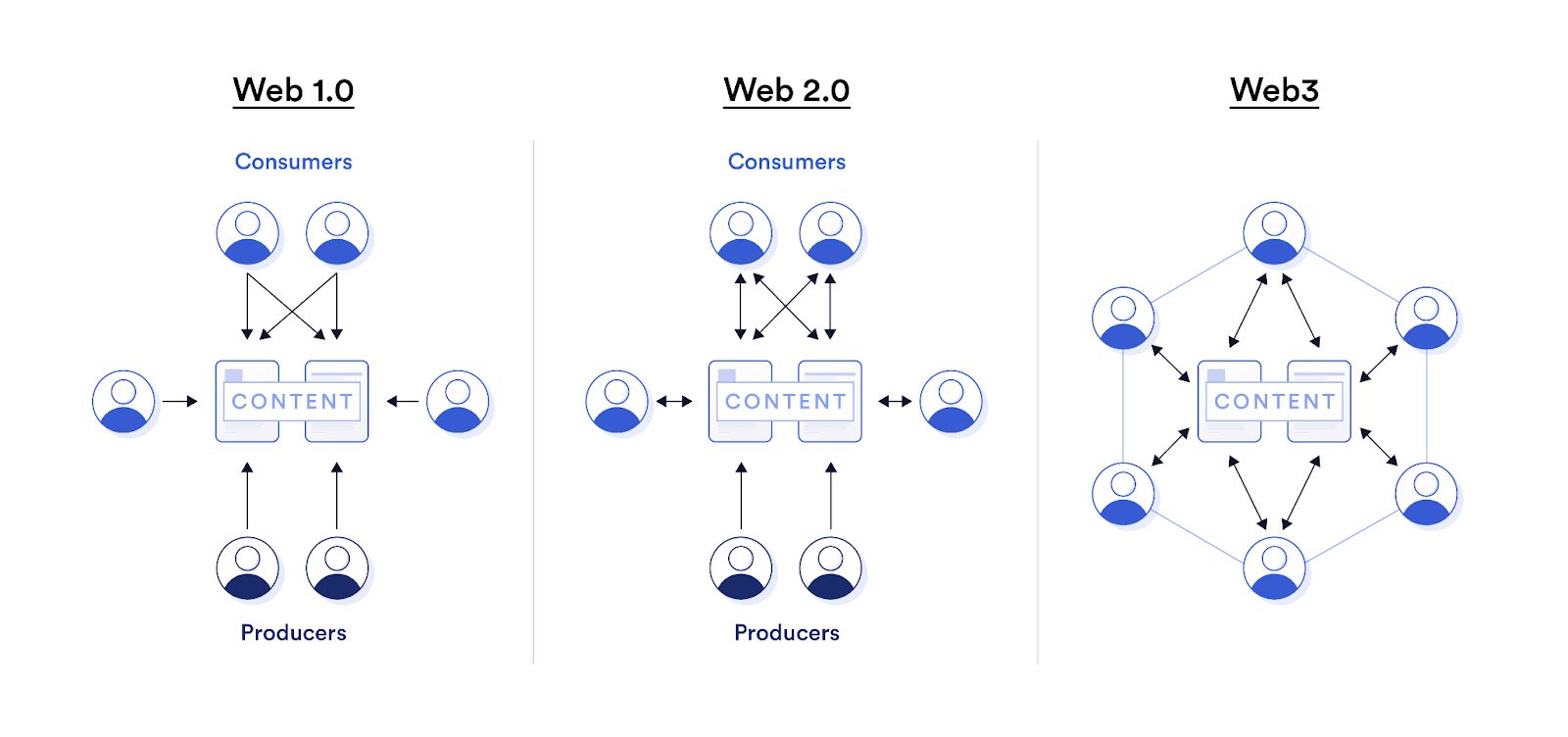
What is the difference between Web3 and Web 3.0?
Web3 and Web 3.0 are often used interchangeably but refer to different concepts. Web 3.0, also known as the semantic web, focuses on making web content more machine-readable, using technologies to enable better data interchange. It aims to create a more intelligent, user-centric web. Web3, on the other hand, refers to a decentralized version of the web based on blockchain technology, focusing on giving users control over their data and decentralizing applications. While both aim to enhance the user experience, the core difference lies in Web3’s emphasis on decentralization and blockchain integration.
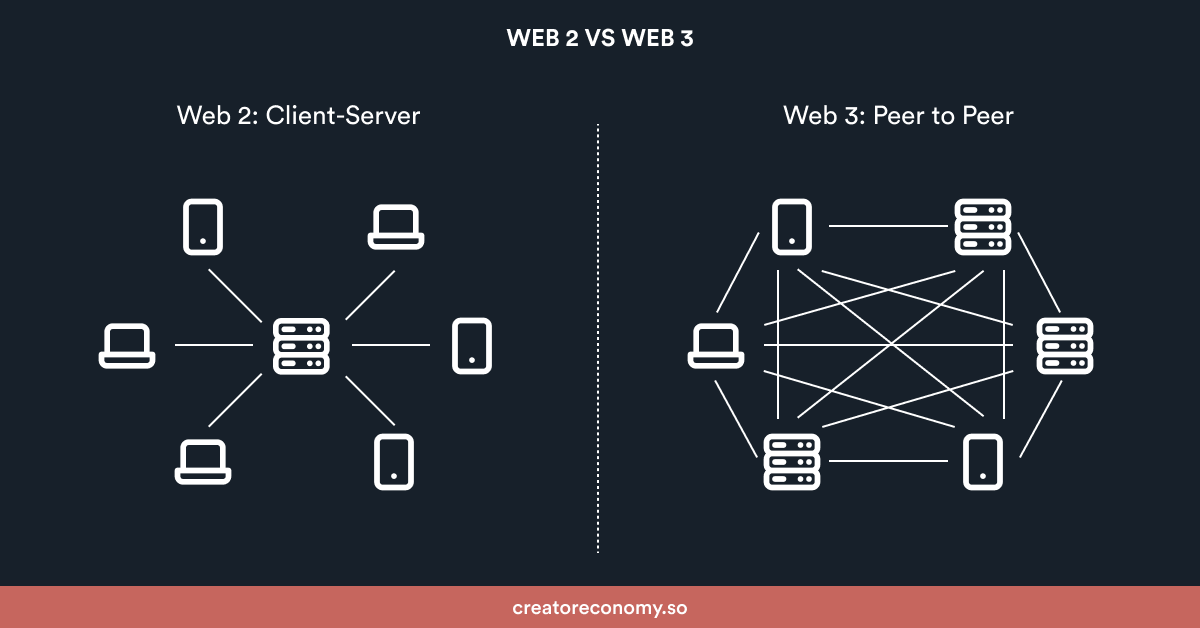
How does Web3 differ from Web 2.0 in terms of user interaction and data ownership?
Web 2.0 marked the evolution from static, read-only web pages to a more interactive web where users can contribute content, communicate through social media, and use applications. However, Web 2.0 centralized control over user data, often in the hands of large corporations. Web3, on the other hand, aims to decentralize the web, allowing users to own their data and interact directly with decentralized applications (dApps). Web3 utilizes blockchain technology to ensure that data ownership and control remain with the users, rather than centralized platforms.
What role does blockchain play in the evolution of Web3?
Blockchain plays a pivotal role in Web3 by enabling the decentralization of the internet. While Web 2.0 relies on centralized servers and corporations to store data, Web3 uses decentralized networks, such as blockchain, to securely store and manage user data. Blockchain’s transparency and immutability ensure that users can control their own data, making Web3 more secure and private. Blockchain-based applications, smart contracts, and decentralized finance (DeFi) are key elements that make Web3 distinct from previous iterations of the web.
How does the concept of a decentralized web differ from the centralized web of Web 2.0?
The concept of a decentralized web, as seen in Web3, contrasts sharply with the centralized web of Web 2.0. In Web 2.0, data and control are concentrated in the hands of large corporations that operate centralized platforms (e.g., social media, cloud services). Web3 envisions a decentralized web where data is stored on multiple nodes across the globe, and users retain ownership and control. Blockchain technology underpins this decentralization, enabling peer-to-peer interactions and eliminating the need for intermediaries. This shift aims to create a more equitable and transparent internet.
What technologies are used to implement Web3, and how do they differ from Web 3.0 technologies?
Web3 is implemented through decentralized technologies such as blockchain, smart contracts, and decentralized storage. Blockchain serves as the backbone of Web3, enabling secure, peer-to-peer transactions and data storage without intermediaries. In contrast, Web 3.0 relies on semantic web technologies, which aim to make data more machine-readable and enhance interaction between applications. Web3 uses blockchain to decentralize control, whereas Web 3.0 uses data interchange technologies to improve web functionality and make content more accessible and intelligent. Both are aimed at enhancing user experience, but Web3 emphasizes decentralization and user ownership.