Understanding the Mechanism Behind Stablecoins: How Do They Work?

In recent years, the landscape of finance has witnessed a remarkable evolution with the advent of digital currencies. These innovative financial instruments have captured the attention of both investors and regulators alike, providing new avenues for transactions and investment. The surge in popularity has sparked conversations about their potential to reshape traditional economic models while offering novel functionalities.
At the core of this revolution lies a specific category of digital assets designed to maintain stability in value. Unlike their more volatile counterparts, these assets aim to offer a reliable means of exchange and preserve purchasing power. This stability is achieved through various strategies that provide a cushion against market fluctuations, making them an appealing option for users seeking consistency in their financial dealings.
Delving deeper into the underlying structures of these stable digital currencies reveals an intricate web of mechanisms. From collateralized models to algorithmic approaches, each framework presents unique characteristics that influence how these currencies operate and maintain their value. Understanding these diverse approaches is essential for grasping the broader implications of their integration into the financial ecosystem.
What Are Stablecoins?
Digital currencies designed to maintain a consistent value offer an intriguing solution in the fast-paced world of cryptocurrencies. By pegging their worth to traditional assets, these tokens aim to minimize volatility and provide a reliable means of exchange.
These digital assets have gained popularity due to several key features:
- Price Stability: The primary goal is to keep the value steady, often aligning with fiat currencies like the US dollar or commodities like gold.
- Accessibility: Users can easily trade or utilize these assets in various financial transactions, enhancing their utility in the market.
- Efficient Transactions: Transactions can be processed quickly and at lower costs compared to traditional banking methods.
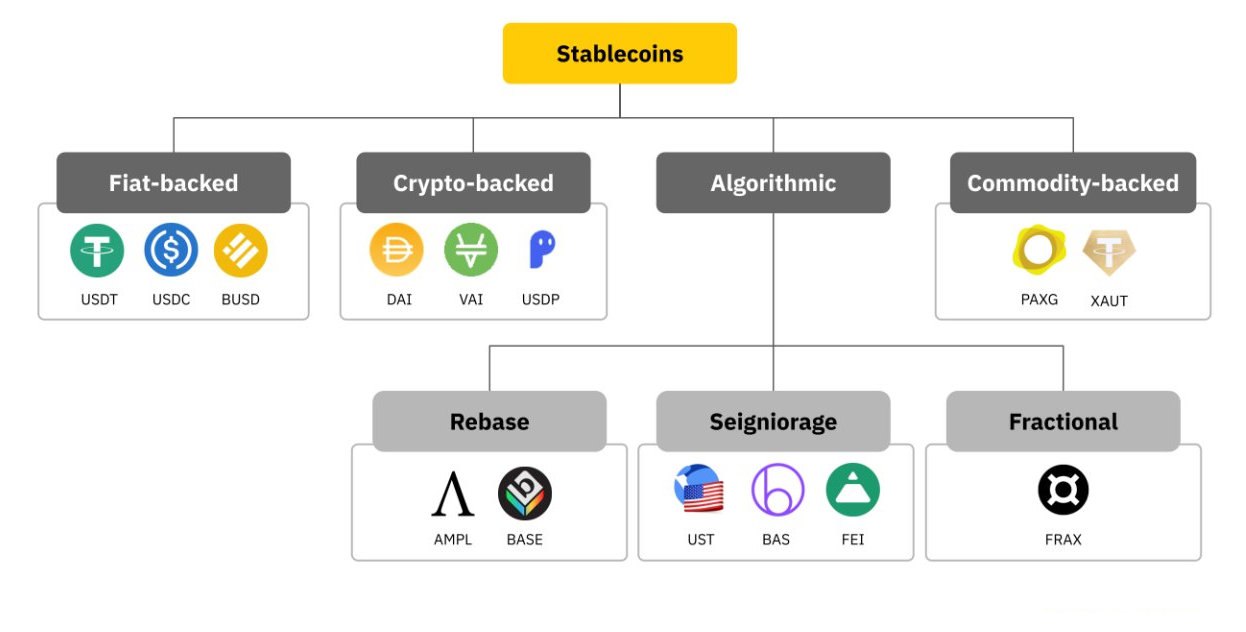
Different types exist, each with unique approaches to achieve this stability:
- Fiat-Collateralized: These are backed by reserves of currency, ensuring that each digital coin is redeemable for a set amount of the underlying asset.
- Crypto-Collateralized: These rely on other cryptocurrencies as collateral, providing over-collateralization to absorb price swings.
- Algorithmic: This type uses smart contracts and algorithms to control supply and demand, dynamically adjusting the circulating amount to stabilize price.
As the cryptocurrency landscape continues to evolve, these digital currencies play a critical role in bridging the gap between the traditional financial ecosystem and the innovative world of decentralized finance.

Types of Stablecoins Explained
This section delves into the various classifications of digital currencies designed to maintain a stable value. Each category has unique characteristics that cater to different needs within the financial ecosystem. Recognizing these distinctions can assist users in selecting the most suitable option for their specific requirements.
Fiat-collateralized variants are directly pegged to traditional currencies, like the US dollar or euro, ensuring stability through reserves held in financial institutions. This structure provides reassurance as it links the value of the digital asset to established monetary systems.
Crypto-collateralized types utilize other digital currencies as collateral. To account for the inherent volatility of cryptocurrencies, these assets are over-collateralized, meaning that the value of the collateral exceeds the value of the stable asset issued. This mechanism aims to balance fluctuations and preserve a consistent worth.
Algorithmic options depend on smart contracts and algorithms to manage supply and demand dynamically. By automatically adjusting the quantity of the currency in circulation based on market conditions, these systems strive to achieve stability without the need for collateral.
Each form offers distinct advantages, highlighting the importance of understanding them to make informed decisions in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
How Stablecoin Mechanisms Work
The functionality of these digital assets revolves around creating a consistent value that mirrors traditional currencies or commodities. By employing various approaches, they aim to minimize price volatility, making them more reliable for everyday transactions and as a store of value. This section delves into the distinct strategies utilized to maintain equilibrium in pricing and user confidence.
Types of Value Anchors
Different types of assets serve as security to ensure stability. Here are some notable types:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Fiat-Collateralized | These are backed by reserves of traditional currency held in a bank account. |
| Crypto-Collateralized | These utilize other cryptocurrencies as collateral, typically over-collateralized to absorb market fluctuations. |
| Algorithmic | These rely on algorithms and smart contracts to manage supply and demand dynamically without backing through traditional assets. |
Maintaining Price Stability
To achieve equilibrium, various mechanisms are implemented, including issuing or burning tokens based on market demand. In collateralized models, adjustments in collateral volume may occur, while algorithmic variants focus on altering supply through smart contract protocols. These systems collectively work to assure that the value remains anchored, providing users with a dependable unit for transactions.
Benefits of Using Stablecoins
Digital currencies designed to minimize volatility provide various advantages for users and the broader financial ecosystem. These benefits can enhance the way transactions are conducted, investments are made, and how financial services are accessed. With a stable value, these currencies become a reliable alternative for both individuals and businesses.
One of the primary advantages is the ability to conduct transactions without the fear of sudden price fluctuations. This reliability allows for easier budgeting and planning, especially in commerce. Furthermore, the reduced volatility promotes trust among users, fostering greater adoption and use in everyday transactions.
Additionally, these currencies often facilitate faster transfers compared to traditional financial systems. By leveraging blockchain technology, transactions can occur instantly across borders, removing intermediaries and associated fees. This efficiency not only saves time but also reduces operational costs for businesses.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Price Stability | Minimized fluctuations in value enable predictable financial planning. |
| Fast Transactions | Instant transfer capabilities cut down on wait times and deliver efficiency. |
| Cost-Effective | Lower fees due to direct transactions eliminate the need for intermediaries. |
| Accessibility | Available to a global audience, promoting financial inclusion. |
| Enhanced Security | Utilization of blockchain technology offers secure and transparent transactions. |
In conclusion, leveraging currencies with stable values can transform financial interactions, offering new possibilities for users across the globe while overcoming some of the limitations of traditional finance.
Challenges and Risks Involved
Within the realm of digital finance, certain hurdles and uncertainties must be navigated. The stability and integration of these financial instruments are influenced by various factors that can introduce vulnerabilities, impacting users and the broader economy. Awareness of these potential pitfalls is crucial for anyone engaging in this domain.
Market Volatility and Liquidity Issues
Despite their design to maintain value, fluctuations in market confidence can lead to unexpected volatility. External events, regulatory changes, and shifts in user sentiment can create liquidity issues, making it challenging to exchange or utilize these instruments effectively. Participants may find themselves exposed to significant financial repercussions during times of instability.
Regulatory Uncertainty
The evolving landscape of regulations surrounding these financial products poses an inherent risk. Governments and authorities worldwide continue to assess and develop frameworks that govern their use. Non-compliance with evolving regulations can result in penalties or restrictions, potentially affecting the viability of the product and its issuers. Understanding the legal implications is essential for participants to mitigate these risks.
Future Trends in Stablecoin Development
The evolution of digital assets designed to maintain a stable value is poised to undergo significant transformations in the coming years. Innovations in technology, regulatory frameworks, and market demand are expected to shape a new landscape where these financial instruments could play a more integral role in both everyday transactions and institutional finance.
Technological advancements will likely drive the next phase of these instruments. As blockchain technology continues to mature, we may see enhanced scalability, privacy, and interoperability features being integrated into new iterations. This could result in a more robust and efficient ecosystem that caters to a diverse range of users, from individuals to large enterprises.
The regulatory environment is another crucial factor influencing future developments. As authorities worldwide recognize the growing significance of these digital assets, clearer guidelines and frameworks are expected to emerge. This regulatory clarity can lead to increased trust among users, fostering wider adoption and integration into mainstream finance.
Moreover, the demand for innovative use cases is likely to grow. As the fintech landscape evolves, opportunities for implementing these digital assets in various sectors, such as remittances, cross-border transactions, and decentralized finance, will expand. This could catalyze the development of specialized offerings tailored to specific industries and consumer needs.

Ultimately, as stakeholders navigate the interplay of technology, regulation, and market requirements, the trajectory of these financial instruments will reshape how value is transferred and stored in the digital era.
Q&A: Stablecoins – How Do They Work?
What are stablecoins and how do they differ from regular cryptocurrencies?
Stablecoins are a type of cryptocurrency designed to maintain a stable value by pegging their worth to a reserve of assets, such as fiat currencies (like the US dollar) or commodities (like gold). Unlike regular cryptocurrencies, which can experience significant price volatility, stablecoins aim to provide a more stable and predictable valuation. This stability is achieved through various mechanisms, including collateralization, algorithmic adjustments, or a combination of both. This makes stablecoins appealing for use in transactions, savings, and as a medium of exchange, as they mitigate the risks associated with price fluctuations typical of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum.
What are the main types of stablecoins and how do their mechanisms function?
There are three main types of stablecoins: fiat-collateralized, crypto-collateralized, and algorithmic stablecoins. Fiat-collateralized stablecoins, like Tether (USDT) or USD Coin (USDC), are backed 1:1 by reserves of fiat currency held in a bank. This means for every stablecoin issued, an equivalent amount of fiat is stored to ensure its value. Crypto-collateralized stablecoins, such as DAI, are backed by other cryptocurrencies held in smart contracts, which are over-collateralized to account for price volatility. Finally, algorithmic stablecoins like Ampleforth use algorithms to control supply and demand to stabilize their price without collateral backing. Each type employs unique mechanisms to achieve stability, appealing to different users and use cases within the financial ecosystem.
What are the risks associated with stablecoins?
While stablecoins offer several benefits, they also come with inherent risks. First, there is the risk of under-collateralization, particularly with crypto-collateralized stablecoins, which can lead to steep losses if the underlying assets experience significant price drops. Second, regulatory risks have emerged as governments consider how to classify and regulate stablecoins, potentially affecting their usability and acceptance. Additionally, issues related to transparency and trust arise in fiat-collateralized stablecoins; if users cannot verify that the issuer maintains sufficient reserves, confidence in the stablecoin can erode. Lastly, algorithmic stablecoins can face challenges in maintaining their pegs during market fluctuations, leading to instability in value. Understanding these risks is crucial for users and investors considering the use of stablecoins.
How can stablecoins be used in everyday transactions?
Stablecoins can be used in a variety of everyday transactions, functioning similarly to traditional currencies but with the advantages of cryptocurrency. They can be utilized for remittances and cross-border transactions due to their lower fees and faster processing times compared to traditional banking systems. Online merchants can accept stablecoins as payments, providing customers with a stable and efficient payment option without the volatility of other cryptocurrencies. Furthermore, stablecoins can facilitate trading on crypto exchanges, where users can convert their assets into stablecoins to lock in profits without exiting the crypto ecosystem. In DeFi (Decentralized Finance) applications, stablecoins are frequently used for lending, borrowing, and yield farming, allowing users to earn interest while maintaining a stable asset value. This versatility makes stablecoins an attractive option for both consumers and businesses.
Are stablecoins truly stable, and how do they maintain their value?
While stablecoins are designed to maintain a stable value, this stability is not always guaranteed. The mechanisms by which they maintain their value vary based on their type. Fiat-collateralized stablecoins typically maintain their peg through a direct 1:1 backing with fiat currency reserves, which is often audited to ensure transparency and trust. Crypto-collateralized stablecoins rely on over-collateralization, meaning they hold more value in collateral than the stablecoins they issue, allowing them to absorb market volatility. Algorithmic stablecoins manage supply and demand through smart contracts that automatically adjust the supply of the stablecoin in response to price changes. Despite these mechanisms, external factors can cause fluctuations; for instance, extreme market conditions or loss of trust in the backing system can lead to a temporary loss of the peg. Therefore, while stablecoins aim for stability, users should remain aware of the risks involved and consider the underlying mechanisms at play.
What are stablecoins and how do they differ from traditional cryptocurrencies?
Stablecoins are a type of cryptocurrency designed to have a stable value, typically pegged to a fiat currency like the US dollar or a commodity such as gold. Unlike traditional cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum, whose values can be highly volatile and subject to speculative trading, stablecoins aim to provide price stability. This stability is achieved through various mechanisms, including collateralization (backing by reserves of fiat or other assets), algorithmic adjustments to supply, or a combination of both. As a result, stablecoins are often used in financial transactions, for trading, and as a means of storing value without the risks associated with more volatile cryptocurrencies.
How do stablecoins work, and why are they important in the crypto market?
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies that are designed to maintain a stable value by being backed by reserves such as fiat money, commodities, or other crypto assets. They are typically pegged to a stable asset like the US dollar, which helps stabilize their value. Stablecoins aim to achieve price stability, making them useful for transactions, as they mitigate the volatility typically associated with other cryptocurrencies. Popular stablecoins, like USDT and USDC, are backed by fiat and are widely used for trading or as a store of value. Because of their stability, stablecoins also facilitate decentralized applications and smart contract functionality within the blockchain ecosystem.
What are the different types of stablecoins, and how are they categorized?
Stablecoins generally fall into three main categories: fiat-backed stablecoins, crypto-backed stablecoins, and commodity-backed stablecoins. Fiat-backed stablecoins are backed by reserves of fiat money, such as the US dollar, and are typically the most common type, with popular examples like USDT and USDC. Crypto-backed stablecoins, on the other hand, are backed by crypto assets, such as Ether or Bitcoin, and use smart contracts to maintain their peg. Commodity-backed stablecoins are backed by physical commodities like gold or silver. There are also algorithmic stablecoins, which aim to maintain their value through supply and demand adjustments, without being backed by collateral.
What are the advantages of investing in stablecoins, and how can they be used?
Stablecoins can be an attractive option for those looking to avoid the volatility of traditional cryptocurrencies while still benefiting from the advantages of the blockchain. Stablecoins maintain a stable value, making them useful for transactions, trading, and storing value. Investors can buy stablecoins to hedge against market fluctuations or as a way to move funds between different exchanges. Additionally, stablecoins can also be used in decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms to earn interest, participate in lending, and exchange their stablecoins for other assets. For those new to crypto, stablecoins 101 provides a clear introduction to their use and benefits.
What is the role of a stablecoin issuer, and how do they manage stablecoins?
A stablecoin issuer is responsible for issuing stablecoins and managing their underlying collateral to ensure that the stablecoin maintains its peg. Stablecoin issuers are typically centralized entities or decentralized systems that oversee the issuance and redemption of the stablecoin. For fiat-backed stablecoins, the issuer holds reserves of fiat money equivalent to the amount of stablecoins in circulation. For crypto-backed stablecoins, the issuer maintains crypto collateral to back the stablecoins issued. The issuer also works to ensure the value of the stablecoins remains stable, and they may employ mechanisms such as regular audits or smart contract code to adjust the supply or demand.
What is the future of stablecoins, and how do they impact the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem?
Stablecoins have become an integral part of the cryptocurrency ecosystem by providing a stable store of value and medium of exchange. The rise of decentralized stablecoins, which are governed by algorithms and smart contracts, represents a shift towards more decentralized finance (DeFi) systems. Many stablecoins are linked to decentralized applications (dApps) and can be used to access DeFi protocols, lending platforms, and decentralized exchanges. The future of stablecoins looks promising as they facilitate easier entry into the crypto market for both individual and institutional investors. As stablecoins maintain their value and improve liquidity, they will continue to play a crucial role in bridging the gap between traditional finance and the crypto world.




