Understanding What Are Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Blockchain Networks

The rise of digital currencies has opened the door to a new dimension of transactions and interactions. This innovative landscape is characterized by direct exchanges between users, eliminating the need for intermediaries and fostering a sense of community engagement. As participants in this digital realm connect, they enable seamless information transfer and enhance the overall reliability and security of the system.
At its core, this transformative model hinges on the cooperation of numerous nodes that form a cohesive unit. Each participant plays a crucial role, contributing to the integrity and continuity of the operations. This collaborative framework not only empowers individuals but also promotes transparency and efficiency across various applications.
In this article, we will delve into the mechanics of these decentralized systems, highlighting the unique characteristics that distinguish them from traditional methodologies. By examining their structure and functionality, we aim to shed light on the potential they hold for reshaping economies and revolutionizing how we perceive value in the digital age.
Overview of P2P Blockchain Architecture
This section delves into the fundamental structure and principles behind decentralized systems that allow for secure and efficient transactions without the need for central authority. The architecture empowers participants to engage directly, fostering an environment where trust is built through consensus mechanisms and distributed ledger technologies.
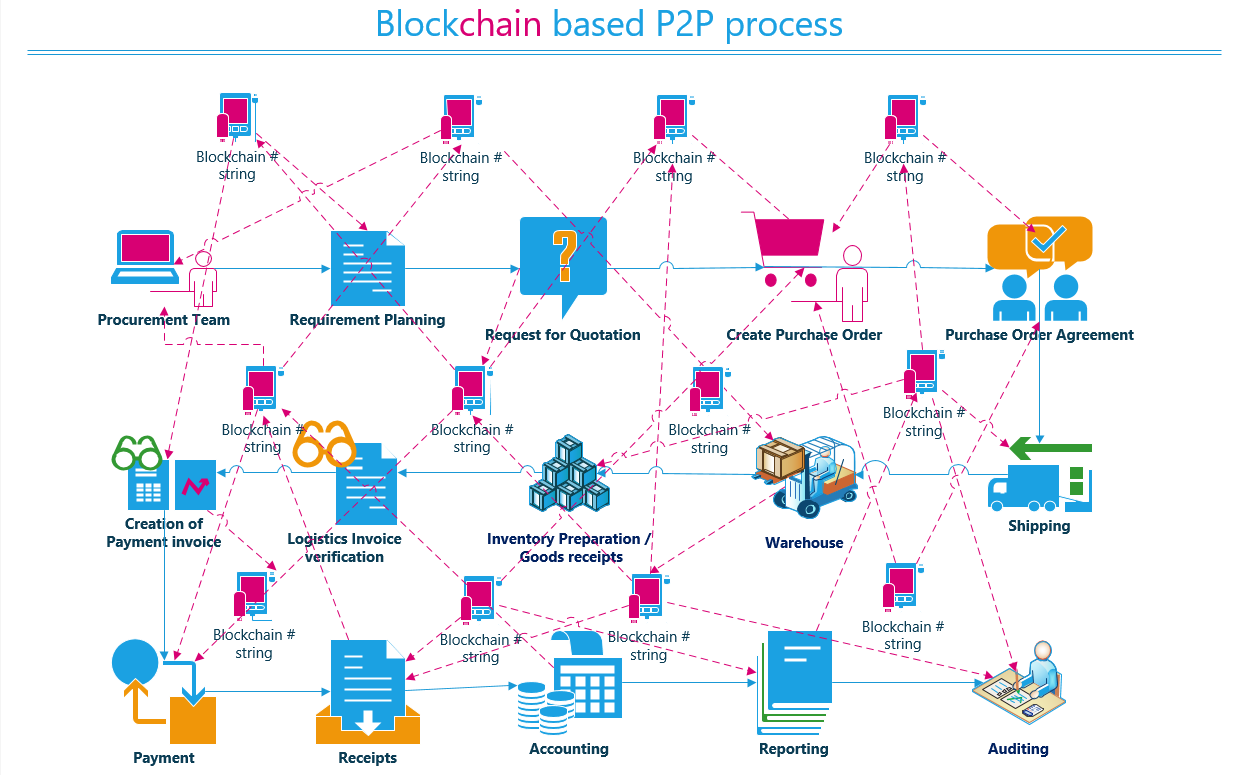
The core elements of this decentralized structure can be categorized into several key components:
- Nodes: Individual participants that maintain a copy of the ledger and validate transactions.
- Distributed Ledger: A shared database that is continuously updated and synchronized across all nodes, ensuring transparency.
- Consensus Mechanisms: Protocols that facilitate agreement among participants on the validity of transactions, crucial for maintaining the integrity of the system.
The interactions among these components create a resilient framework that enhances security and reliability. The absence of a central authority not only decentralizes control but also minimizes vulnerability to single points of failure.
Key benefits of this innovative architecture include:
- Enhanced security through cryptographic techniques.
- Increased transparency, as all transactions are publicly accessible.
- Improved efficiency, as there is no need for intermediaries.
- Reduced operational costs stemming from streamlined processes.
Understanding the interplay between these elements equips participants with insights into how decentralized systems operate and evolve, opening up new possibilities for applications across various industries.
Key Features of Decentralized Networks
Decentralized systems embody a fundamental shift from traditional architectures by distributing control across numerous participants. This model enhances resilience and promotes egalitarian participation, leading to a more robust and secure ecosystem.
Enhanced Security
One of the most significant advantages of distributed systems is their inherent security. By eliminating a single point of failure, these architectures reduce the risk of attacks. Each participant holds a copy of the shared data, making unauthorized modifications exceptionally challenging. Cryptographic techniques further bolster this security, ensuring that information exchanges remain confidential and tamper-proof.
Greater Autonomy and Transparency
In a decentralized framework, individuals have greater control over their assets and transactions. This autonomy fosters trust among participants, as actions are recorded in a transparent manner. Decision-making processes are often collective, minimizing the influence of central authorities and enabling equal participation. Such openness encourages community involvement and can lead to innovation driven by shared interests.
Advantages of Peer-to-Peer Technology
This innovative approach to digital interactions offers a variety of benefits that enhance efficiency, security, and accessibility. By enabling direct connections between participants, it fosters an environment where resources can be shared without relying on centralized authority.
Decentralization is one of the most prominent features, promoting autonomy among users. Without a central entity controlling the system, individuals are empowered to make decisions and transact freely, reducing the risk of single points of failure.
Cost-effectiveness is another noteworthy advantage. By eliminating intermediaries, users can reduce transaction fees and operational costs. This efficiency is especially advantageous for small businesses and individuals seeking to minimize expenses.
Furthermore, privacy and security are greatly enhanced. Direct connections limit exposure to potential data breaches or hacks. Participants can maintain greater control over their personal information, ensuring that data is only shared with trusted parties.
Scalability is also a crucial aspect. As more users join the system, the network becomes stronger and more resilient. This growth creates opportunities for increased collaboration and resource availability, ultimately benefiting all members.
In summary, these key advantages make this technology an attractive alternative for those seeking efficient, secure, and cost-effective solutions in their digital interactions.
Common Use Cases for P2P Blockchains
Decentralized digital systems have gained remarkable traction across various sectors due to their ability to enhance transparency, security, and efficiency. These innovative platforms allow participants to interact directly, facilitating seamless exchanges and transactions without the need for intermediaries. In this section, we will delve into several prevalent applications that showcase the versatility and effectiveness of these technologies.
One of the most notable applications is in the realm of financial services, where cryptocurrencies are used for peer-to-peer transactions. These digital currencies enable users to send and receive funds quickly and at lower costs compared to traditional banking methods. Furthermore, decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms are redefining access to financial products, granting individuals the ability to lend, borrow, and trade assets without reliance on central authorities.
Supply chain management is another area where these modern systems have proven advantageous. By utilizing transparent ledgers, companies can enhance traceability and accountability throughout the supply chain. Every transaction and movement of goods can be securely recorded, allowing businesses to quickly identify sources of delays or discrepancies, thus optimizing their operations.
Additionally, digital identity management stands out as a critical use case. Individuals can own and control their digital identities, enabling secure verification processes without the need for centralized databases. This approach not only enhances privacy but also reduces the risk of identity theft and fraud.
Moreover, the entertainment industry is embracing these technologies to enable direct content distribution. Artists can monetize their work without intermediaries, ensuring that a larger share of revenue goes directly to them. This shift empowers creators and fosters a more equitable ecosystem for content sharing.

Finally, the realm of voting and governance benefits from these innovations by introducing greater transparency and security to electoral processes. Utilizing decentralized systems for casting votes can help prevent fraud and ensure that results are verifiable, thereby increasing trust in democratic systems.
Challenges Facing P2P Blockchain Systems
The innovative architecture of decentralized systems has brought forth numerous advantages, but it also encounters a variety of obstacles that can hinder its widespread adoption and functionality. As such frameworks become more prevalent, understanding these challenges is crucial for developers, users, and stakeholders who aim to harness their full potential.
Scalability Issues
One of the primary hurdles faced by decentralized platforms is scalability. As the number of participants increases, the workload on the network grows, leading to slower transaction speeds and higher processing times. This can create bottlenecks, making it difficult for the system to efficiently handle a large volume of activities while maintaining the quality of service expected by users.
Security Vulnerabilities
Despite their inherent security features, decentralized systems are not impervious to attacks. Vulnerabilities can arise from various sources, including smart contract bugs, network partitions, and the potential for a malicious actor to gain control over a significant portion of the network. Ensuring robust security measures is vital to protect assets and maintain user trust in the ecosystem.
The Future of Peer-to-Peer Networks
The evolution of decentralized systems heralds a transformative era where individuals can connect directly, facilitating seamless interactions and transactions. As technology continues to mature, these systems are poised to reshape various industries, offering innovative solutions to age-old challenges. The trajectory of these frameworks points towards increased efficiency, transparency, and user empowerment.
As more individuals become aware of the benefits associated with direct exchanges, the demand for such solutions is likely to rise. This shift could lead to the development of platforms that prioritize privacy and security, fostering environments where participants can confidently engage. The integration of advanced cryptographic techniques will further solidify trust among users, ensuring that transactions remain secure and verifiable.
By harnessing collective resources, upcoming iterations of these systems may redefine concepts like ownership and governance. The potential for collaborative decision-making can enable communities to take charge of their digital assets, promoting a sense of shared responsibility. Furthermore, innovations in scalability and interoperability will enhance the user experience, making participation more accessible than ever.
In conclusion, the pathway towards more interconnected environments reflects not only technological advancement but also a societal shift towards decentralization. As these systems continue to evolve, they promise to unlock new possibilities, empowering individuals and communities on a global scale.

Q&A: What Are P2P Blockchain Networks?
What are P2P blockchain networks and how do they work?
P2P (peer-to-peer) blockchain networks are decentralized networks where each participant, or node, in the network has equal authority and responsibility. Unlike traditional centralized systems where a central authority controls the data, P2P networks enable direct interactions between users. Each node maintains a copy of the entire blockchain, allowing for transparency and security. When a transaction is made, it is broadcast to all nodes that validate the transaction through consensus algorithms. Once validated, the new block is added to the blockchain, and all nodes update their copies, ensuring that the information is consistent across the network.
What are the benefits of using P2P blockchain networks over traditional centralized systems?
The benefits of P2P blockchain networks include increased security, transparency, and resilience to failures or attacks. In a centralized system, if the central server is compromised, sensitive data can be lost or stolen. However, in a P2P network, data is distributed among numerous nodes, making it difficult for malicious actors to corrupt the entire system. Additionally, transparency is enhanced since all transactions are visible to every participant, fostering trust among users. Moreover, P2P networks are inherently more resilient to single points of failure, as the network can continue to operate as long as some nodes remain functional.
How can I set up a node in a P2P blockchain network?
Setting up a node in a P2P blockchain network generally involves several steps, which can vary depending on the specific blockchain platform you choose. First, download the blockchain software relevant to that network. This could be Bitcoin Core, Ethereum, or another blockchain system. Once installed, you’ll need to configure the software to connect to the network by adjusting the settings to specify your bandwidth, storage, and other preferences. Then, allow the software to synchronize with the network to download the entire blockchain history. After synchronization, your node will be active and participate in the network, helping to validate and relay transactions.
What are some common challenges faced by P2P blockchain networks?
P2P blockchain networks encounter several challenges, including scalability, security risks, and energy consumption. Scalability poses a significant issue as the number of transactions increases; some networks may struggle to process large volumes efficiently. Additionally, while P2P networks enhance security against certain attacks, they are not immune to issues like Sybil attacks, where an adversary creates multiple identities to disrupt the network. Furthermore, many blockchain networks, especially proof-of-work systems, require substantial energy to maintain the network, raising concerns about environmental sustainability. These challenges necessitate ongoing research and innovation to enhance the effectiveness of P2P blockchain technologies.
What is the role of consensus algorithms in P2P blockchain networks?
Consensus algorithms are critical in P2P blockchain networks as they enable all nodes to agree on the validity of transactions and the state of the blockchain. These algorithms ensure that despite the decentralized nature of the network, there is an established method for reaching an agreement. Common types of consensus algorithms include Proof of Work (PoW), where nodes solve complex mathematical problems, and Proof of Stake (PoS), where validators are chosen based on the number of coins they hold. The consensus mechanisms help prevent double-spending and ensure that all participants have a consistent view of the shared ledger, enhancing the reliability and security of the network.
What are P2P blockchain networks and how do they work?
P2P blockchain networks, or peer-to-peer blockchain networks, are decentralized networks where each participant (or node) interacts directly with one another without the need for an intermediary. In these networks, every participant has equal authority and responsibilities, which enhances security and reduces the risk of a single point of failure. By leveraging cryptographic techniques, transactions in a P2P blockchain are recorded in a public ledger, making them transparent and immutable. When a transaction occurs, it is validated by multiple nodes through consensus mechanisms, such as proof of work or proof of stake, ensuring that all participants agree on the state of the network. This design fosters trust, as all changes to the blockchain are publicly verifiable and permanent. Overall, P2P blockchain networks promote peer interaction, efficiency, and transparency in data sharing and transaction processing.
What is the difference between unstructured p2p and structured p2p networks?
Unstructured p2p networks do not have a predefined structure and rely on a random connection between peers, meaning that peers in the network are not aware of all other peers. In contrast, structured p2p networks use a distributed hash table (DHT) to manage and organize the connections between nodes. This structure allows peers to find other peers and resources more efficiently. The unstructured p2p network may be less efficient in finding specific peers compared to the more organized structured p2p networks, but it can be more flexible in terms of network participation.
How does a hybrid p2p network combine the features of both unstructured and structured networks?
A hybrid p2p network combines the strengths of both unstructured and structured networks by integrating a more flexible peer-to-peer architecture with the organized approach of a structured network. In a hybrid p2p network, some peers may operate in a structured manner using a distributed hash table (DHT), while others may join or leave the network in a more unstructured manner. This allows for a more adaptable network where peers can choose the level of organization they prefer while maintaining some level of efficiency in resource discovery.
What role does the peer-to-peer architecture play in crypto networks?
In p2p crypto networks, the peer-to-peer architecture is crucial because it enables decentralized trading and communication without relying on a central server. Peers in the network cooperate to validate transactions and distribute data, such as blockchain copies or transaction history. The decentralized nature of p2p networks means that transactions are directly conducted between peers, offering greater privacy and reducing the risk of centralized control or failure. This architecture is also vital in p2p crypto exchanges, where users can trade digital assets directly without intermediaries.
How do p2p networks distribute blockchain data and enable cryptocurrency transactions?
P2p networks distribute blockchain data by allowing nodes to replicate the entire blockchain or relevant sections of it across multiple peers. When a new peer joins the network, it may download the blockchain data from other active peers. Each node participates in validating transactions, ensuring that transactions on the network are legitimate without requiring a central server. The distributed nature of p2p crypto networks enables faster transaction processing and enhances the security of the blockchain by ensuring that every peer has a copy of the entire blockchain, making it resistant to censorship and fraud.
What are the limitations of p2p networks, and how do they affect their use in blockchain technology?
P2p networks have limitations such as scalability issues, network congestion, and potential security risks. Since each peer in the network must maintain a copy of the blockchain and validate transactions, large networks may face challenges with data synchronization and transaction throughput. Additionally, the decentralized nature of p2p networks can sometimes lead to slower transaction processing or reduced reliability when peers leave the network unexpectedly. Despite these limitations, p2p networks are still fundamental to blockchain technology, offering enhanced decentralization and reducing reliance on central authorities. However, the network’s efficiency and scalability must be optimized to handle growing adoption and transaction volumes.


