Understanding the Differences Between Bitcoin vs Bitcoin Cash – BTC and BCH

Amid the dynamic landscape of digital currencies, a particular rivalry has captured the attention of enthusiasts and investors alike. This ongoing debate revolves around two prominent forms of decentralized monetary systems, each boasting unique attributes and functionalities. As the popularity of these alternatives continues to soar, understanding their core principles becomes crucial for anyone venturing into the realm of virtual assets.
These two notable contenders emerged from a shared foundation, yet they diverge significantly in terms of operational mechanics and target audiences. Each currency presents distinct approaches to transaction processing, scalability, and community governance, offering users varied experiences based on their preferences and needs. By delving into these aspects, one can grasp the nuances that set them apart and appreciate the innovations that each brings to the table.
As we peel back the layers of this fascinating topic, it becomes clear that the choice between these two currencies is not merely a matter of preference, but one that reflects different philosophies and visions for the future of money. With a focus on pivotal characteristics, this exploration aims to illuminate the contrasts that define these innovative financial instruments, guiding potential users and investors toward informed decisions.
Origins and Creation of Bitcoin Variants
The inception of various digital currencies stems from the desire to enhance the original framework and address certain limitations faced by the first cryptocurrency. The evolution of these currencies is marked by technological advancements and community-driven decisions, leading to diverse implementations. The narrative of these alternatives illustrates a broader quest for scalability, transaction speed, and innovative features that cater to the ever-growing needs of users and investors alike.
Initial Developments
The initial variant emerged due to the community’s recognition of challenges related to transaction processing times and fees. As the user base expanded, congestion became a pressing issue, prompting discussions within the community about possible solutions. This led to a fork, where developers and users collectively determined the direction and features of the new blockchain. The creation of this alternative represented a significant divergence in philosophy concerning network size and operation.
Community Influence
The journey of these variants has often been influenced by the passionate views of their respective communities. Ideological differences regarding scalability and usability paved the way for further innovations. The governance models adopted also played a crucial role, as stakeholders sought to implement solutions that fit their vision of an ideal digital currency. This dynamic interplay among users, developers, and investors continues to shape the landscape of alternative currencies today.
Technical Differences in Block Size
The sizes of blocks play a crucial role in the performance and scalability of various cryptocurrency networks. Variations in block size directly influence transaction speeds, confirmation times, and the overall efficiency of the system. This section delves into the specifics of how differing block capacities can lead to varied experiences for users and miners alike.
Block Size Specifications
The specifications set for blocks can determine how many transactions are processed simultaneously. Here are the primary points of distinction:
- One network may utilize a smaller block size, which can result in congestion during peak times.
- Another network often adopts a larger block size, allowing for a higher transaction throughput.
Impact on Transactions
The implications of these block size standards are significant for transaction handling:
- A smaller block may lead to longer wait times for confirmations as users compete to have their transactions included.
- A larger block size can improve transaction speed, enabling quicker processing and lower fees during busy periods.
Ultimately, the technical variations in block capacities shape the user experience and network efficiency, influencing both individual transactions and the broader ecosystem. Understanding these aspects is essential for navigating the landscape of digital currencies.
Transaction Speed and Confirmation Times
The efficiency with which transactions are processed and the duration required for their validation are crucial factors in the world of digital currencies. These elements can significantly impact user experience, influencing both everyday transactions and the long-term viability of different platforms.
Factors Affecting Speed
Several components play a role in determining how quickly transactions are executed:
- Block Size: Larger blocks can accommodate more transactions, potentially reducing wait times.
- Network Congestion: High demand can lead to slower processing as miners prioritize transactions based on fees.
- Mining Difficulty: Adjustments in mining requirements can affect how quickly blocks are added to the chain.
Confirmation Times Comparison
Confirmation times, which indicate how long it takes for a transaction to be verified on the network, vary markedly:
- Initial Confirmation: The first acknowledgment of a transaction’s inclusion in a block.
- Final Confirmation: The time taken for subsequent blocks to reinforce the security of that transaction.
Ultimately, a solid grasp of how speed and confirmation affect user interactions is essential for making informed choices in the evolving landscape of digital currencies.
Community and Ecosystem Support Comparisons
A thriving ecosystem is essential for the success and sustainability of any digital currency. The strength of community involvement plays a significant role in shaping development, usage, and overall acceptance. Various factions engage in promoting and enhancing the respective platforms through grassroots initiatives, discussions, and technological advancements.
Each currency boasts a distinct community that influences its evolution and utility. Supporters frequently contribute to development, provide educational resources, and foster a sense of belonging among users. By analyzing these components, one can gain insights into how community dynamics affect each network.
| Aspect | Network A | Network B |
|---|---|---|
| Community Size | Large with diverse participants | Smaller but highly dedicated |
| Development Contributions | Numerous open-source projects and proposals | Focused contributions from a core group |
| Advocacy and Promotion | Active campaigns and meetups | Online forums and educational initiatives |
| Partnerships | Wide range of collaborations | Selected strategic alliances |
| Public Perception | Generally positive with broad recognition | Growing reputation among niche audiences |
Understanding the support systems surrounding each currency provides valuable insights into their respective trajectories and future potential. As technology evolves, these communities will continue to play a pivotal role in driving innovation and adaptation within their ecosystems.
Use Cases: What Each Coin Offers
This section will delve into the distinct functionalities and applications of two prominent digital currencies. Each currency presents unique features that cater to varying needs within the cryptocurrency ecosystem. Understanding these applications is crucial for individuals and businesses considering their adoption.
The first currency emphasizes scalability and transaction speed, aiming to facilitate everyday transactions efficiently. Its ability to handle a higher volume of transactions at lower fees makes it an attractive option for merchants looking to integrate digital payments into their business models. Additionally, its focus on simplicity can enhance user experience, making it more accessible for newcomers to the world of cryptocurrency.
The second currency, in contrast, prioritizes an extensive network effect and aims to serve as a digital store of value. Advocates argue that its structure encourages long-term investment and wealth preservation, appealing to users who view it as a hedge against inflation. With a mindset centered on creating a robust financial alternative, this currency finds favor among individual investors and institutional players alike.
Ultimately, both currencies contribute to the evolving landscape of digital finance, each carving out its niche in a diverse and rapidly changing market. Users must evaluate their specific needs and preferences to determine which option aligns best with their financial goals.
Investment Perspectives for Users
When exploring the realm of digital currencies, it is essential for individuals to assess the various options available and their potential for financial gain. Different varieties of digital assets offer unique opportunities and challenges, influencing investment strategies and outcomes. Understanding these aspects can empower users to make informed decisions that align with their financial goals.
Risk Tolerance plays a vital role in determining which digital currency might be a better fit for an investor. Some may prefer assets with higher volatility for the chance of substantial returns, while others might opt for more stable alternatives to minimize risks. Thus, users should evaluate their personal risk thresholds to guide their investment choices.
Furthermore, market trends and technological advancements can significantly impact the desirability of certain assets. Staying updated on the latest developments in the ecosystem is crucial, as it informs users about potential price fluctuations and the driving forces behind them. This awareness can help in making timely investment decisions.
Diversification is another important strategy for those looking to navigate the digital currency landscape. By spreading investments across a range of assets, users can mitigate overall risk and increase the likelihood of positive returns. A well-thought-out portfolio can enhance stability in an otherwise fluctuating market.
Lastly, long-term vs. short-term strategies must be considered when engaging with digital currencies. Investors may choose to hold their assets for an extended period, betting on long-term growth, or make quick trades to capitalize on short-lived opportunities. Each approach has its merits and can be tailored to suit individual financial aspirations and market conditions.

Q&A: Bitcoin vs Bitcoin Cash – Key Differences
What are the primary differences between Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash?
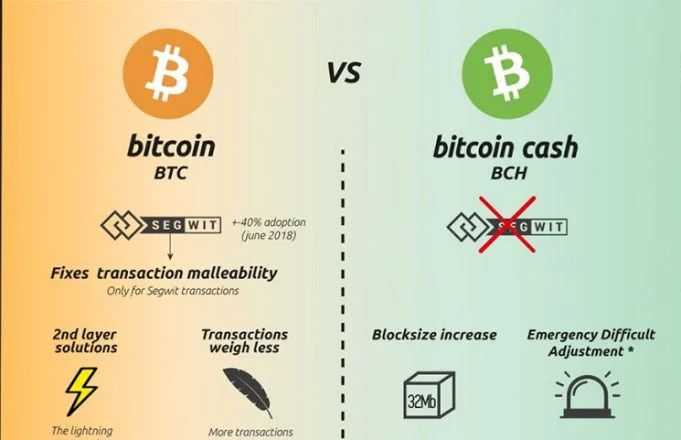
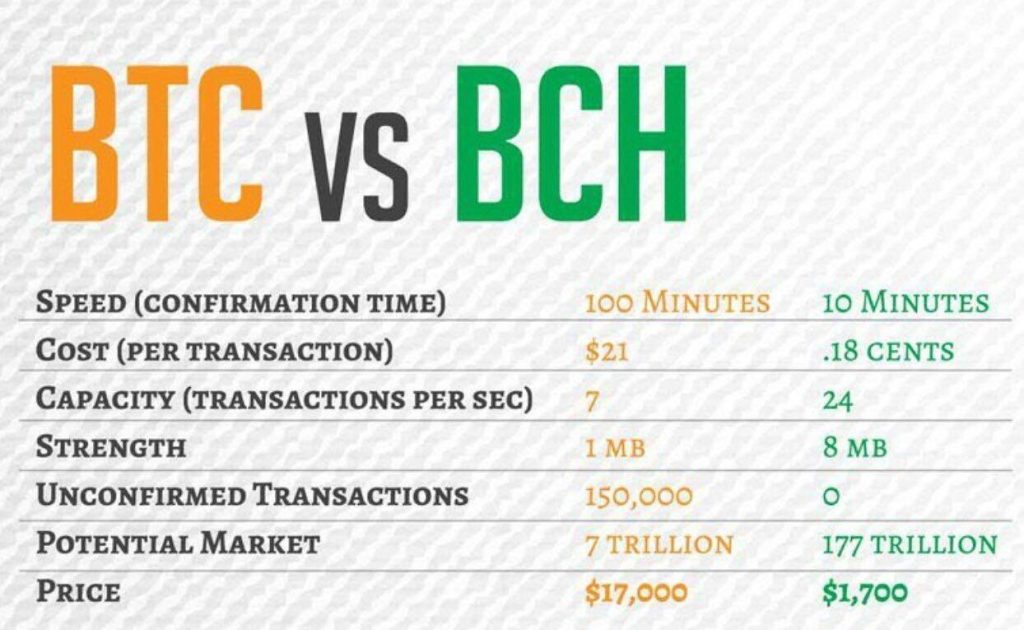
Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash mainly differ in their block size and transaction processing capabilities. Bitcoin’s block size is limited to 1 MB, which can lead to slower transaction times when the network is congested. In contrast, Bitcoin Cash was created to increase the block size limit to 8 MB (and later to 32 MB), allowing for more transactions to be processed simultaneously. This difference aims to enhance scalability and make daily transactions more efficient. Additionally, Bitcoin prioritizes being a store of value, while Bitcoin Cash focuses on being a peer-to-peer electronic cash system.
Why was Bitcoin Cash created, and what problem does it aim to solve?
Bitcoin Cash was created in August 2017 as a result of a hard fork from Bitcoin. The main motive behind its creation was to address the scalability issues that Bitcoin faced due to its limited block size. During periods of high demand, Bitcoin transactions could take longer to confirm, which made it less practical for everyday use as cash. Bitcoin Cash seeks to resolve this by allowing larger blocks, thereby facilitating faster transactions and reducing fees, thus enabling it to be used more effectively for everyday purchases.
How do transaction fees compare between Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash?
Transaction fees for Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash vary significantly, especially during peak network usage times. Bitcoin generally experiences higher fees due to its limited block size, which can lead to congestion and a bidding war for transaction confirmations. In contrast, Bitcoin Cash’s larger blocks allow for lower fees under similar conditions. As a result, users often find that sending Bitcoin Cash is more cost-effective, particularly for smaller transactions, making it more accessible for daily transactions and micro-payments.
What are the implications for investors when considering Bitcoin vs Bitcoin Cash?
Investors should consider the differing philosophies and potential use cases of Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash. Bitcoin is often viewed as “digital gold,” a store of value, appealing to those looking for long-term investment on the premise of rarity and security. In contrast, Bitcoin Cash targets everyday transactions, which may attract users interested in practical applications of cryptocurrency for daily spending. Furthermore, investors should also analyze market volatility, adoption rates, and community support, as these factors can significantly affect the investment potential of each cryptocurrency. Overall, investors might choose based on whether they prioritize value storage (Bitcoin) or transactional functionality (Bitcoin Cash).
Can you explain how developers and the community view the future of Bitcoin versus Bitcoin Cash?
Developers and community members have distinct visions for the future of Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash. The Bitcoin community generally focuses on enhancing security, scaling solutions like the Lightning Network, and maintaining Bitcoin’s status as a reliable store of value. They believe that a more secure and stable network will facilitate broader adoption over time. Conversely, the Bitcoin Cash community aims to prioritize scalability on-chain and accessibility for everyday transactions, envisioning a future where cryptocurrency is widely used for purchases in a manner similar to traditional cash. This difference reflects their unique priorities, leading to ongoing debates about the best approach for cryptocurrency’s role in society.
What led to the creation of bitcoin cash as a fork of bitcoin?
Bitcoin cash was created in 2017 as a hard fork of bitcoin to address scaling issues within the bitcoin network. The debate within the bitcoin community centered around transaction speed and fees, with one group advocating for an increase in the block size to allow more transactions per block. Bitcoin cash increased the block size to 8 MB, compared to bitcoin’s original 1 MB, enabling faster processing of transactions per second and lower fees. This split marked a significant divergence in how the two cryptocurrencies would evolve.
What are the key differences between bitcoin cash and bitcoin?
The key differences between bitcoin cash and bitcoin lie in their approach to scalability and transaction speed. Bitcoin cash increased the block size to allow more transactions per second, making it suitable for use as digital cash. Bitcoin, however, remains focused on security and decentralization, with a smaller block size and higher fees for transactions. Bitcoin cash also uses different protocols for block validation, while bitcoin continues to follow the original vision for bitcoin’s blockchain. These differences make bitcoin cash better suited for day-to-day payments, whereas bitcoin is often considered a store of value.
How does bitcoin cash handle transactions per second compared to bitcoin?
Bitcoin cash can process more transactions per second compared to bitcoin due to its larger block size. With a block size of 32 MB, bitcoin cash allows for more transactions to be included in each block, reducing congestion and keeping transaction fees low. In contrast, bitcoin’s smaller 1 MB block size limits the number of transactions that can be processed, resulting in slower confirmation times and higher fees, especially during periods of high demand.
What is the original vision for bitcoin, and how does bitcoin cash aim to fulfill it?
The original vision for bitcoin, as outlined by its creator, was to be a peer-to-peer digital cash system. However, as bitcoin gained popularity, scalability issues and high transaction fees made it less practical for everyday use. Bitcoin cash was created to fulfill this original vision by increasing the block size, enabling faster transactions with lower fees. Supporters of bitcoin cash believe that it stays closer to the original concept of bitcoin as a medium of exchange rather than a store of value.
What’s the difference between bitcoin cash and bitcoin sv?
Bitcoin cash and bitcoin sv both originated from the same fork of bitcoin in 2017, but bitcoin sv further forked from bitcoin cash in 2018. The primary difference is their approach to scalability and protocol changes. Bitcoin sv increased the block size limit even further, aiming for massive scalability and enterprise adoption, whereas bitcoin cash focuses on maintaining a balance between usability and decentralization. Both cryptocurrencies share a similar goal of improving transaction processing but differ significantly in their technical implementations and long-term visions.

