Understanding Data Tokenization and Its Importance in Security

In today’s digital landscape, safeguarding sensitive information is paramount. With the increasing prevalence of cyber threats, organizations are compelled to adopt innovative strategies that shield private data from unauthorized access. This approach often involves substituting critical elements with non-sensitive alternatives, ensuring a robust mechanism for maintaining confidentiality.
Such replacements not only mitigate risks but also facilitate compliance with regulatory standards. By employing a method that obfuscates original details, entities can maintain operational efficiency while securing customer trust. Furthermore, this practice enhances overall resilience, allowing businesses to navigate the complexities of contemporary data handling challenges.
As the focus on privacy intensifies, the importance of advanced protective measures becomes evident. Organizations that effectively implement these transformative strategies position themselves as leaders in the quest for a secure informational environment. Recognizing the value of innovative techniques for safeguarding assets is essential for long-term success in a rapidly evolving digital world.
What is Data Tokenization?
In today’s digital landscape, safeguarding sensitive information has become paramount. Organizations are continually seeking innovative measures to enhance privacy while facilitating operations. One approach gaining traction involves the substitution of critical information with non-sensitive equivalents, enabling businesses to minimize risk.
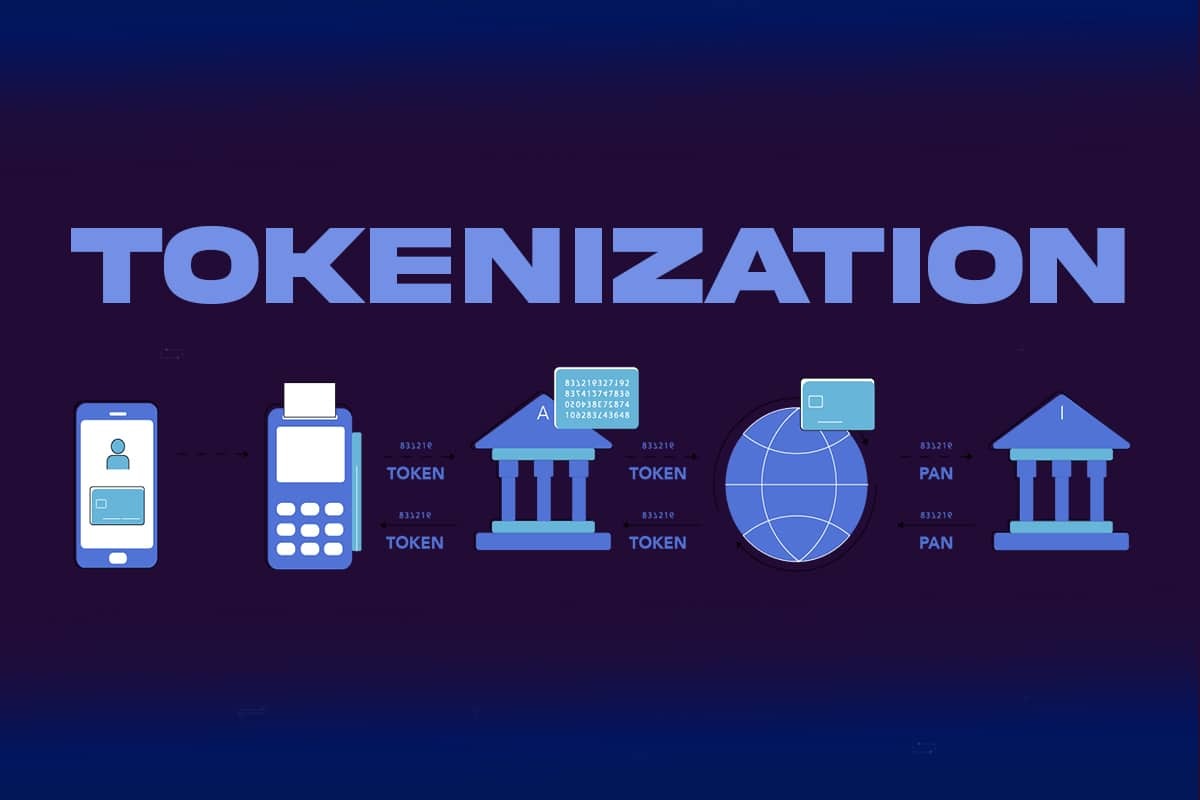
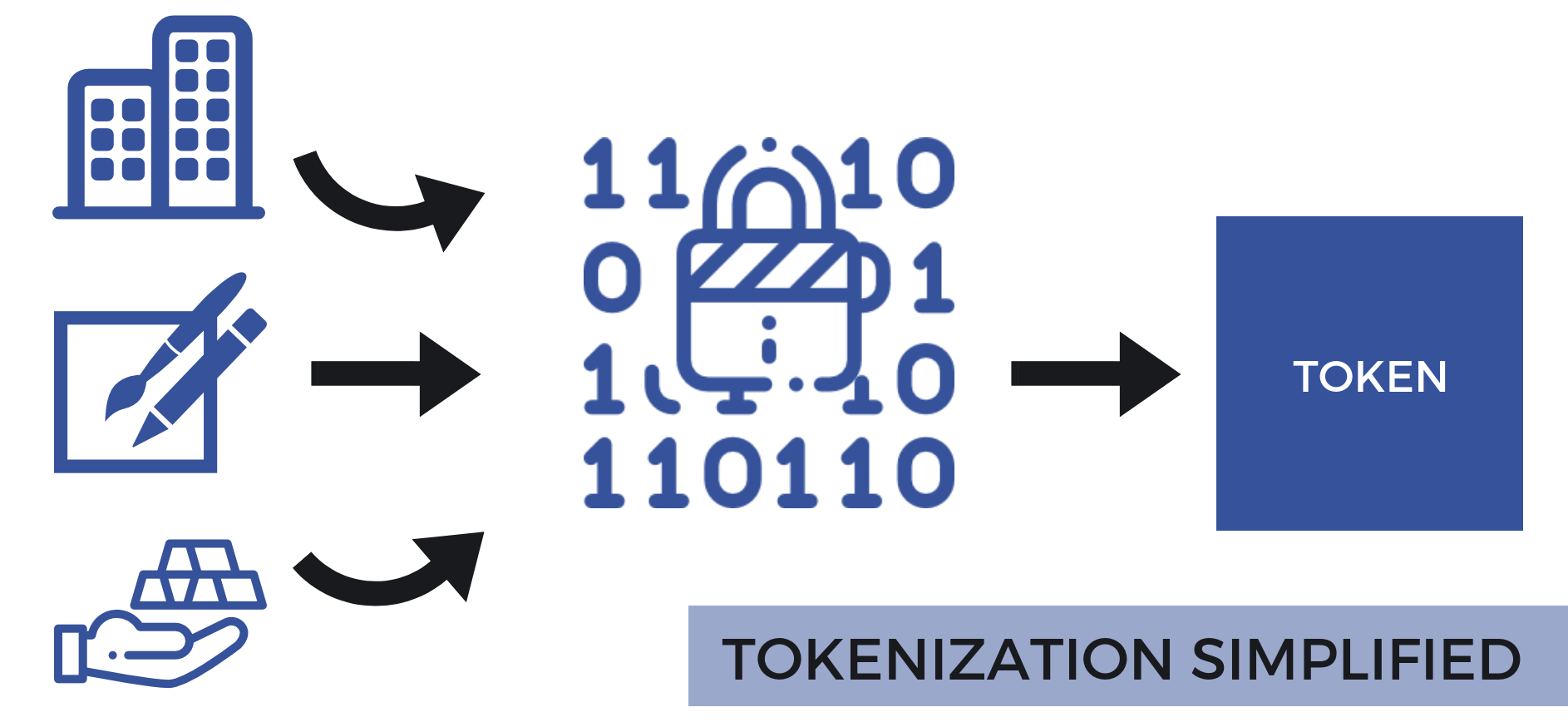
This practice involves the transformation of valuable identifiers into unique, non-identifiable symbols that retain essential details without compromising security. These substitutes allow entities to work with data without exposing the original content.
- Reduction of security breaches
- Compliance with regulations
- Preservation of usability for analytics
By implementing this method, companies can effectively mitigate the potential consequences associated with unauthorized access. The core idea revolves around maintaining functionality while significantly lowering the risk profile.
- Identification of sensitive information
- Replacement with non-sensitive tokens
- Secure storage of original data
With the rise in cyber threats, the necessity for such preventive strategies becomes increasingly evident, providing a formidable line of defense against potential vulnerabilities.
How Tokenization Enhances Data Privacy
Utilizing advanced techniques to safeguard sensitive information is paramount in today’s digital landscape. This approach transforms identifiable details into non-sensitive equivalents, enabling organizations to protect valuable data while maintaining functionality in their systems. The process minimizes exposure, ensuring that even if breaches occur, the compromised information remains inconsequential.
Key Advantages of This Method
- Reduced Risk: By substituting sensitive elements with tokens, the actual data remains secure, significantly lowering the likelihood of unauthorized access.
- Compliance: Firms can meet regulatory requirements more effectively by implementing these protection measures, reducing legal liabilities associated with data loss.
- Controlled Access: Access to tokenized information can be tightly regulated, establishing a robust framework for information governance.
Implementation Considerations
- Integration: Incorporating this technique into existing systems may require careful planning to ensure functionality.
- Management: Token management strategies must be developed to maintain security and facilitate retrieval when necessary.
By adopting these methodologies, organizations can achieve a higher standard of confidentiality, aligning with both consumer expectations and industry standards.
Comparing Tokenization with Encryption
Both techniques serve to safeguard sensitive information, yet they operate through distinct methodologies. While one seeks to obscure data content, the other offers a means of transforming it into an unreadable format. Understanding these approaches is essential for selecting the right solution for specific needs.
Encryption is a widely recognized process that converts readable information into a format that cannot be comprehended without a decryption key. This means that with the appropriate key, the original data can be restored. Conversely, substitution replaces sensitive elements with non-sensitive equivalents, known as tokens, which have no meaning outside the specific context in which they are used.
When weighing these alternatives, consider the level of protection required and the implications of each method. Encryption can be reversed if the decryption key is obtained, which may pose risks if keys are compromised. On the other hand, substitution does not allow for direct recovery of the original data from the tokens, enhancing security in high-stakes environments.
Additionally, the operational impacts should be evaluated. Encryption often requires computational resources for processing, while substitution can streamline transactions by allowing the original data to remain securely stored and separated from the operational environment.
Ultimately, the choice between these security measures should depend on the specific requirements of the organization, including compliance mandates, the sensitivity of the information, and the desired level of operational efficiency.

Key Benefits of Implementing Tokenization
Adopting a method to safeguard sensitive information has become a priority for many organizations. This approach not only enhances security but also optimizes operational processes while ensuring compliance with industry regulations. By substituting critical data elements with non-sensitive equivalents, businesses can reduce their exposure to various threats.
Enhanced Protection Against Breaches
One of the primary advantages of this technique is the significant reduction in risk of data breaches. By replacing identifiable information with tokens, even if attackers gain access to the system, they are met with useless substitutes that hold no real value. This ensures that the core data remains shielded, providing an additional layer of defense against unauthorized access.
Compliance and Risk Management
Compliance with regulatory standards is a critical aspect for any enterprise handling sensitive information. By implementing this protective measure, organizations can more easily adhere to laws and regulations that mandate the safeguarding of personal and financial details. This proactive stance not only mitigates potential penalties but also fosters trust among clients and stakeholders.
Challenges in Data Tokenization Deployment
The implementation of replacement techniques within organizations presents several hurdles that must be navigated to achieve effective safeguarding of sensitive information. Despite the advantages offered, several complexities can arise during the deployment process.
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Integration with Existing Systems | The necessity to blend new solutions with pre-existing technological infrastructures can lead to compatibility issues, complicating the setup. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Organizations must ensure that their new measures align with industry regulations, which can vary significantly across different regions. |
| Performance Overheads | The introduction of such measures might introduce latency or performance costs that can affect system efficiency if not managed properly. |
| Staff Training | Personnel must be adequately trained to handle new protocols and tools, which can require additional resources and time. |
| Potential Mismanagement | Improper implementation or oversight of new processes can lead to vulnerabilities, negating the purpose of the safeguarding techniques. |
Overcoming these obstacles requires careful planning, thorough training, and a clear strategy to leverage the protective capabilities while minimizing interruptions to existing workflows.
Future Trends in Data Security Solutions
The landscape of protection mechanisms is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing sophistication of cyber threats. Emerging techniques and tools are paving the way for enhanced safeguarding of vital information, addressing both current challenges and anticipating future needs. As organizations strive to fortify their defenses, innovative strategies are expected to redefine the approach to information integrity and confidentiality.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence is set to play a crucial role in revolutionizing protective measures. Machine learning algorithms will enable systems to analyze vast amounts of information in real-time, identifying suspicious activities and potential vulnerabilities with remarkable accuracy. Predictive analytics will enhance the ability to foresee threats, allowing proactive responses that significantly reduce risks. This shift toward automating threat detection and response will empower organizations to maintain a robust security posture in an increasingly complex digital environment.
Rise of Zero Trust Architecture
The adoption of zero trust models is gaining momentum as entities recognize the limitations of traditional perimeter-based defenses. This philosophy emphasizes continuous verification of users and devices, irrespective of their location. By assuming that threats may exist both inside and outside the network, organizations can implement stringent access controls and micro-segmentation. This approach minimizes the attack surface and bolsters resilience against breaches, making it a vital trend in the future of protective infrastructures.
Q&A: What is data tokenization
What is data tokenization and how does it work?
Data tokenization is a data protection technique that replaces sensitive information with unique identification symbols or tokens. These tokens retain all the essential information about the data without compromising its security. The original sensitive data is stored in a secure token vault, while the tokens can be used in applications and databases for processing. When needed, these tokens can be converted back to their original form by authorized systems. This process helps in minimizing the risk of data breaches as the sensitive information is not exposed in day-to-day operations.
What are the key benefits of using data tokenization for data security?
The key benefits of data tokenization include enhanced security, compliance with regulations, and reduced risk of data breaches. By replacing sensitive data with tokens, organizations significantly decrease their exposure to potential cyber threats during transactions. Moreover, since the original data is securely stored and inaccessible during day-to-day operations, companies can align more easily with data protection regulations like GDPR and PCI-DSS. Finally, tokenization can simplify compliance audits and mitigate the impact of a data breach since the stolen data would be in the form of tokens, which are worthless without access to the token vault.
How does data tokenization differ from encryption?
While both data tokenization and encryption are used to protect sensitive information, they operate differently. Encryption transforms data into an unreadable format using algorithms and keys, but the original data can be restored if the proper key is available. On the other hand, tokenization replaces the sensitive data with a non-sensitive equivalent (token) that has no intrinsic meaning. Tokenization operates on the premise that only the tokenization system or token vault can reverse the process. Therefore, tokenization fundamentally eliminates sensitive data from the environment, whereas encryption retains the sensitive data in an encoded form. This makes tokenization often more secure and compliant as it minimizes risk exposure.
Is data tokenization suitable for all types of data?
Data tokenization is most effective for protecting sensitive personal information, such as credit card numbers, social security numbers, and other personally identifiable information (PII). However, not all data types are suitable for tokenization. For instance, data that requires continuous access or is not deemed sensitive may not warrant tokenization due to the complexity and administrative overhead involved. Organizations should assess their specific data protection needs and the nature of the data before implementing tokenization. In addition, it is important to consider the implications for data usability, as excessive tokenization of non-sensitive information may hinder operations.
How does tokenization work to protect sensitive data in the payment card industry data security standard?
Tokenization replaces sensitive data, such as cardholder data, with non-sensitive tokens. These tokens are stored securely, separating the original data from the token, ensuring compliance with payment card industry data security standard and reducing the risk of exposure.
What are the key use cases for a tokenization solution in securing personal data?
Tokenization solutions are commonly used to protect sensitive data in payment transactions, healthcare records, and data warehouses. By replacing sensitive data elements like credit card data with tokens, organizations can safeguard sensitive data and comply with data privacy regulations.
How does tokenization differ from traditional encryption in securing cardholder data?
While encryption protects data by transforming it into encrypted data using an encryption algorithm, tokenization replaces sensitive data with tokens that have no exploitable value. Tokenization may offer a higher level of security for specific use cases, as it reduces data access to the original data.
What benefits does tokenization offer for data analytics in a data warehouse?
Tokenization allows businesses to perform data analytics without exposing sensitive data. By using tokenized data, organizations can analyze trends and patterns securely while maintaining compliance with data privacy regulations and minimizing the risk of sensitive data exposure.
How does the tokenization process help comply with data privacy regulations and protect data in transit?
The tokenization process involves replacing sensitive data with secure tokens, ensuring that real data is not exposed during transit or storage. This approach safeguards sensitive data within systems and aligns with data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA.



